Figure 2.
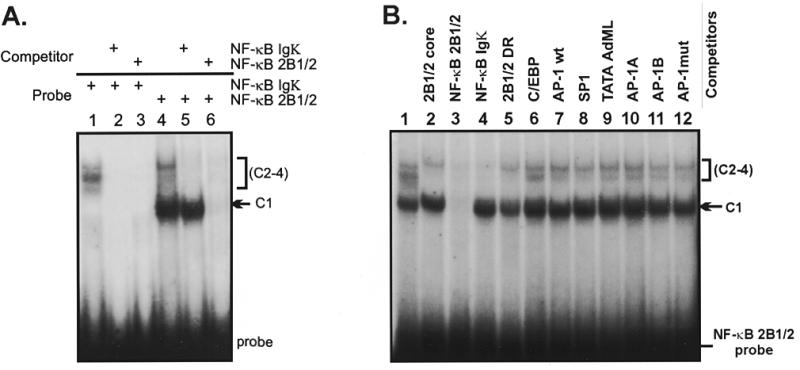
(A) The NF-κB element from the rat CYP2B1/2 MaLR LTR forms several shifted complexes in rat liver nuclear extracts. Band shift reactions contain probes for NF-κB Igκ (lanes 1–3) or NF-κB 2B1/2 (lanes 4–6), as shown. One major complex (C1) and up to three minor complexes (C2–C4) were observed. Addition of unlabeled oligonucleotide competitors NF-κB Igκ (lanes 2 and 5) and NF-κB 2B1/2 (lanes 3 and 6) indicate that the C1 complex is competed by the NF-κB 2B1/2 site, but not the NF-κB Igκ site. (B) C1 complex formation is specific for the NF-κB 2B1/2 element. Reactions were performed using the NF-κB 2B1/2 probe as described in (A). Oligonucleotide competitors include none (lane 1), 2B1/2 core –43 to –13 (lane 2), NF-κB 2B1/2 (lane 3), NF-κB Igκ (lane 4), 2B1/2 DR (lane 5), C/EBP (lane 6), AP-1 (lane 7), Sp1 (lane 8), AdML TATA (lane 9), AP-1-like site A (lane 10), AP-1-like site B (lane 11) and an AP-1 mutant (lane 12). The upper C2–C4 complexes are competed by both the NF-κB 2B1/2 and NF-κB Igκ oligonucleotides (lanes 3 and 4), while competition for the C1 complex is seen only with NF-κB 2B1/2 (lane 3).
