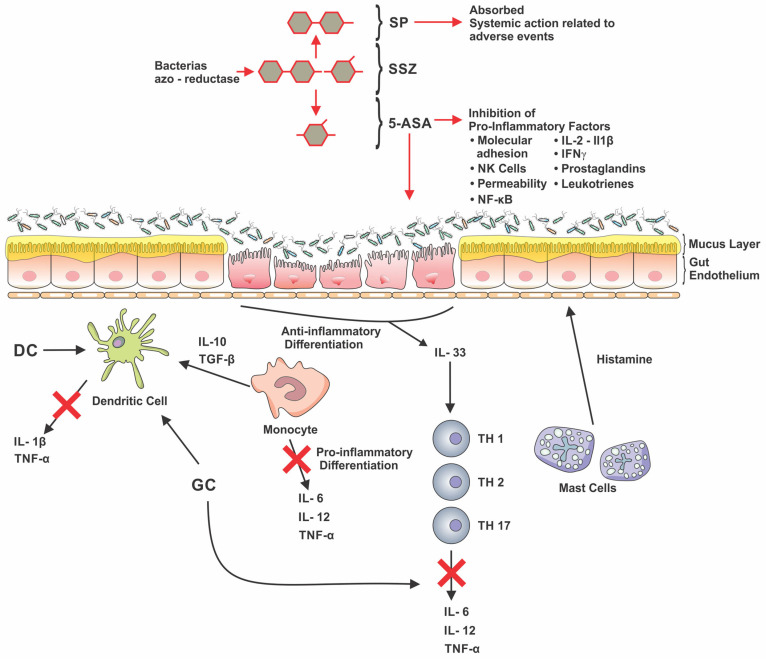
Figure 2.
Action of salicylates and glucocorticoids in IBD. 5-ASA acts on pro-inflammatory factors such as molecular adhesion, Natural Killer cell activation, intestinal permeability, nuclear factor kappa B activation, IL-1β, IL-2, Interferon gamma, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes. Sulfasalazine is converted by bacterial azo-reductases into 5-ASA, the UC-acting moiety, and into Sulphapyridine, which is absorbed and is generally associated with adverse events. Glucocorticoids downregulate the inflammatory cascade by reducing cytokines (represented by the red crosses) such as IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-12, TNF-alpha, in addition to allowing the release of regulatory cytokines such as IL-10. DC: Dendritic cell. GC: glucocorticoids. IL: interleukin. IFN: interferon. NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B. NK: Natural Killer cells. SP: sulfapyridine. SSZ: sulfasalazine. TGF-β: transforming growth factor beta. TH: T helper. TNF: tumor necrosis factor. 5-ASA: 5-aminosalicylate.