Figure 2.
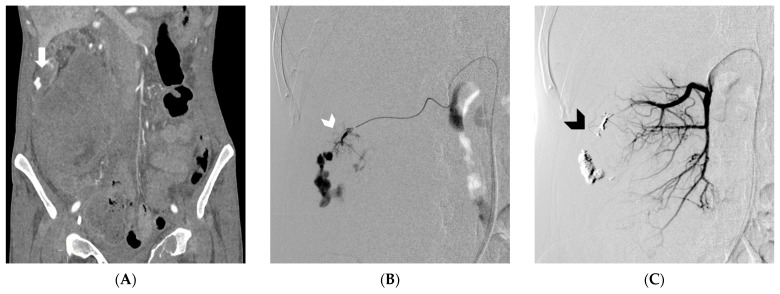
In Figure (A), Computed Tomography angiography reveals spontaneous retroperitoneal bleeding attributed to a ruptured pseudoaneurysm (indicated by the arrow) originating from a renal tumor. Figure (B) shows digital subtraction angiography, which confirms the presence of a ruptured pseudoaneurysm arising from a feeding artery of the tumor (white arrowhead). Lastly, Figure (C) displays digital subtraction angiography, illustrating the successful embolization achieved using an Ethylene-Vinyl Alcohol copolymer cast (indicated by the black arrowhead). (From Minici et al. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040710, by MDPI, Basel, Switzerland, licensed under CC BY 4.0).