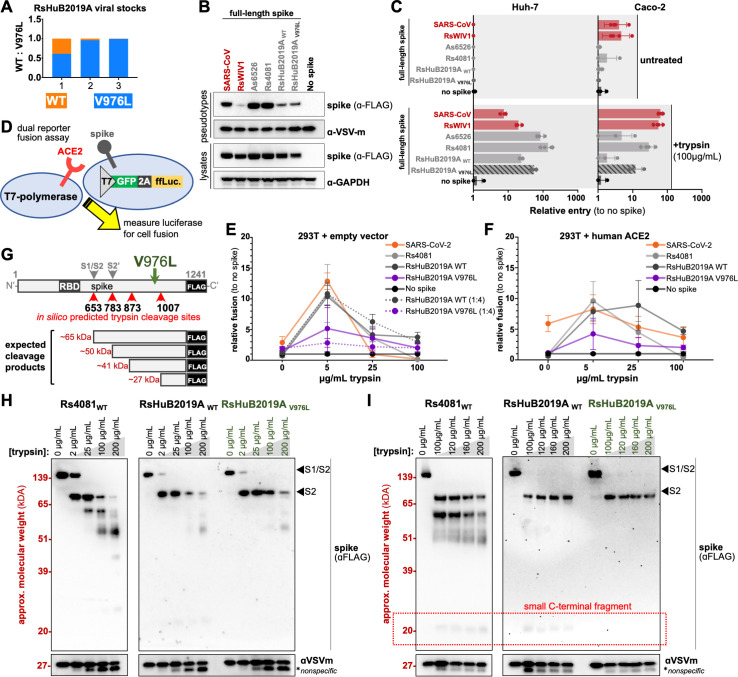
Fig 3.
Clade 2 RBD virus adaptation to the cell culture. (A) V976L mutation emerged in RsHuB2019A virus stocks. (B) Pseudotyped virus particles were produced with full-length spike wild type (WT) or the V967L mutant. Spike was detected in producer cells and pseudotyped virus particles by western blot for FLAG. (C) Indicated cells were infected with pseudotyped virus particles in the presence or absence of trypsin. (D) Schematic overview of the dual-reporter fusion assay developed for this study. T7 polymerase drives the expression of GFP and luciferase separated by self-cleaving 2A peptide from porcine teschovirus-1 (P2A). (E) HEK 293T cells expressing receptor or (F) empty vector and T7 polymerase were combined with cells expressing spike and the T7-driven reporter. Luciferase was measured as a readout for cell fusion. Dotted lines indicate data from 1:4 ratio of receptor: spike cells. (G) Overview of RsHuB2019A spike with in silico predicted trypsin digest sites indicated. Location of V976L is indicated in green. (H) Concentrated pseudotyped virus particles were combined with a wide range of trypsin dilutions or (I) a fine range of trypsin dilutions and incubated at 37°C. Spike digestion was assessed by western blot for the FLAG epitope.