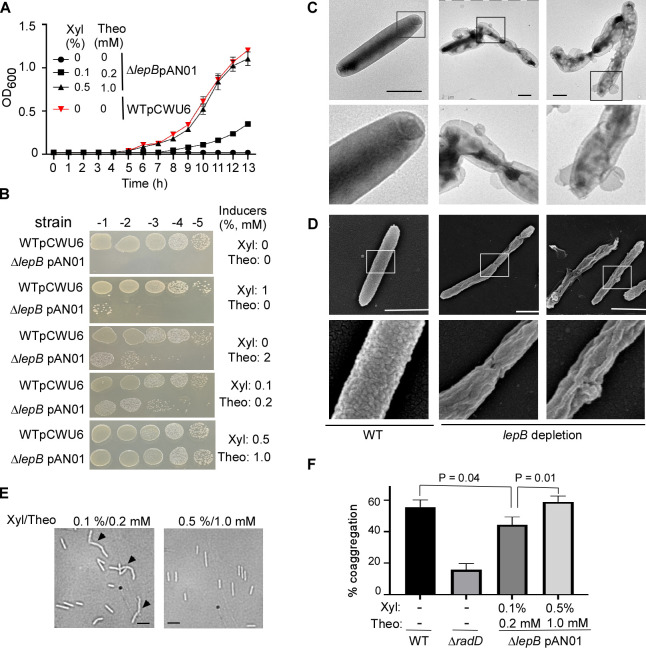
Fig 5.
The type I signal peptidase lepB in F. nucleatum is an essential gene. (A) The effect of inducer(s) on the growth of conditional lepB mutants in the liquid media. F. nucleatum strains (wild-type: strain ATCC 23726 harboring an empty vector pCWU6 (red triangle); lepB conditional mutant: ∆lepB pAN01) were grown statically under anaerobic conditions on TSPC media with various doses of inducers (xylose and theophylline). Turbidity was monitored at an optical density of 600 nm. Data represented the means of SD of the results of triplicate biological experiments. (B) The effects of inducer(s) on the growth of conditional lepB mutants in solid media. Ten-fold serial dilutions of overnight cultures of the wild-type 23726 and the conditional ∆lepB strains were spotted on agar plates with and without inducer(s) xylose and theophylline and cultivated in an anaerobic chamber at 37°C. Cell growth was recorded after 3 days of incubation. (C) LepB depletion creates short filaments and alters outer membrane structures. The lepB-depleted and lepB-inducing cells were immobilized on carbon-coated nickel grids and stained with 0.1% uranyl acetate before viewing with a transmission electron microscope. Enlarged areas of the top panels are shown in the bottom panels. Bars, 1 µm. (D) The altered cell surface of conditional lepB mutant was revealed by scanning electron microscopy. The cells from lepB depletion or lepB induction were immobilized on a silicon wafer and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde before viewing by a scanning electron microscope. Enlarged areas of the top panel are shown in the below panels. Bars, 1 µm. (E) Comparison of lepB conditional mutant strain morphology. Cells were grown under two distinct conditions with inducers (0.1% xylose/0.2 mM theophylline and 0.5% xylose/1.0 mM theophylline). Microscopic examination was conducted after cells reached the stationary phase to assess morphological differences. (F) The quantitative coaggregation assay was performed by mixing wild-type F. nucleatum, radD, and lepB mutants with an equal number of A. oris cells in the coaggregation buffer (CAB). The mixture was allowed to aggregate for 20 minutes before measuring the OD600 absorbance. Measurements were taken both before and after the aggregation process. The presented data represent the average of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test with GraphPad Prism software.