FIGURE 5.
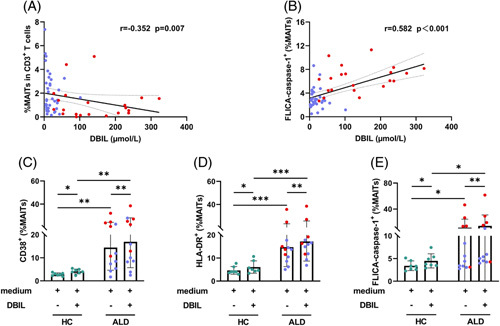
Exposure to DBIL-induced MAITs’ activation and pyroptosis. (A, B) Correlation analysis of MAITs’ frequencies or pyroptotic MAITs’ frequencies and plasma DBIL level in patients with ALC and patients with ALC + SAH. The frequencies of MAITs were negatively correlated with plasma levels of DBIL, and the frequencies of pyroptotic MAITs were positively correlated with plasma levels of DBIL. (C–E) PBMCs from HCs, patients with ALC, and ALC + SAH were treated with medium only and DBIL for 72 hours, respectively. Frequencies of CD38, HLA-DR, and FLICA caspase-1 expressed on MAITs were determined by flow cytometry. The levels of CD38, HLA-DR, and caspase-1 expressed by MAITs significantly increased after DBIL stimulation. The levels of CD38, HLA-DR, and FLICA caspase-1 on MAITs in patients with ALD were higher than those in HCs after DBIL stimulation. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. (A, B) Spearman rank correlation test. (C–E) Wilcoxon signed-rank test and nonparametric Mann-Whitney U tests. Abbreviations: ALC, alcohol-associated liver cirrhosis; ALC + SAH, ALC complicated with severe alcoholic hepatitis; ALD, alcohol-associated liver disease; DBIL, direct bilirubin; HC, healthy control; MAITs, mucosal-associated invariant T cells; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
