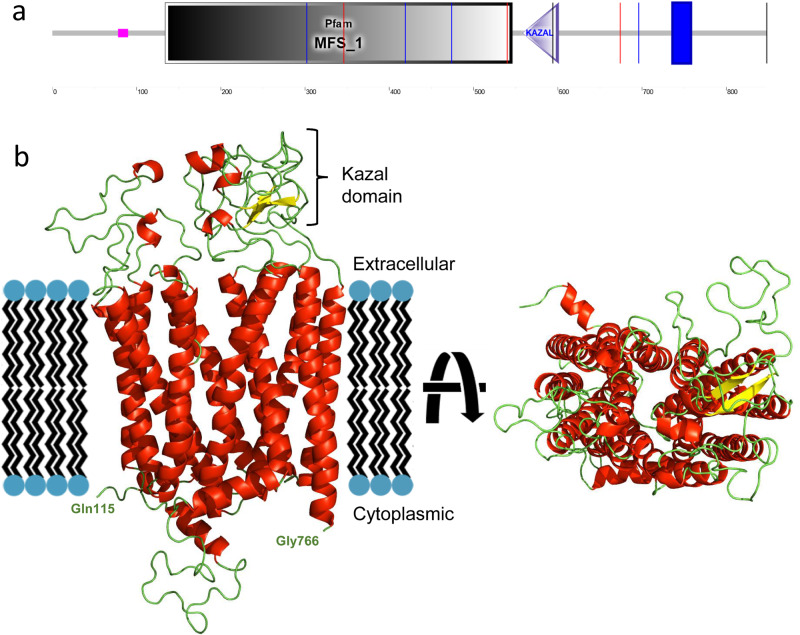
Fig. 3. Domain architecture of human SLCO5A1.
a Schematic representation of the protein with the indication of recognised domains. A SMART analysis to identify structural domains confirmed the presence of two modules, Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) and a Kazal domain, interspaced with potentially unstructured sequences. The MFS transporters are membrane proteins capable of transporting small solutes in response to chemiosmotic ion gradients72,73. They are represented in many organisms from Archaea to Homo sapiens. MFS proteins target a wide range of substrates, including ions, carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids and peptides, nucleosides and other small molecules and transport them in both directions across the membrane74. The Kazal domain is an evolutionary conserved module usually acting as a serine-protease inhibitor. b Predicted model of the monomeric form of SLCO5A1 from amino acids 115–766, built using the SwissModel homology server (https://swissmodel.expasy.org) and utilising the template structure pdb:7eeb. Red: alpha helices; Yellow: Beta strands; Green: Loops.