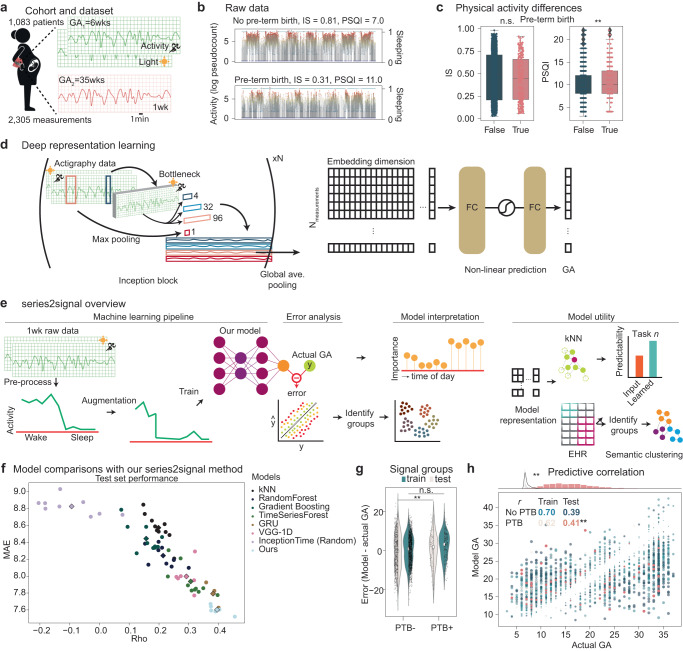
Fig. 1. Overview of series2signal, a method to monitor pregnancy by applying deep learning to data from wearable devices.
a N = 1083 patients were monitored during pregnancy. b Examples of pre-processed actigraphy data drawn randomly from a pregnancy that resulted in preterm birth (bottom) and a term pregnancy (top), as well as the interdaily stability (IS) and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) values for each patient. Green dots indicate binary sleep periods (right axis) per timepoint while dot color on the traces indicate the intensity of activity at a particular instance (left axis). c The distribution of IS and PSQI in the full cohort for preterm birth (PTB+) or term birth (PTB-). d series2signal model architecture showing the number of Inception blocks (in this study, N = 9), and 1D convolutional filters applied to the multivariate time-series input followed by global average pooling to a non-linear representation of actigraphy data that we feed through an adapted prediction block to output a prediction of GA given 1wk of actigraphy data. e The series2signal machine learning pipeline, with a novel data augmentation scheme to limit over-fitting, and associated modules for error analysis, model interpretation in-light of associated error groups and metadata, and model utility with respect to predictability of series2signal’s learned representations and semantic clustering for phenotyping patients based on their actigraphy data. f series2signal outperforms various machine learning methods and is significantly better than random, suggesting that we can monitor pregnancy from wearables data alone. Mean absolute error (MAE) of the model relative to the actual GA of measurements in the test set versus the correlation between the model’s prediction and actual GA is visualized. Diamond markers indicate the average across trials, which are represented as dots in the scatter-plot. g Comparison of the error of the top-1 series2signal model on this cohort showing over-fitting between the train and test sets for pre-term birth vs. the term birth group. h series2signal top-1 predicted GA versus actual GA for the train set (scatter-plot) with Spearman’s ρ correlation shown for each group split by PTB+/PTB- and train/test set (colors). Point size is scaled by the absolute error of that observation (model output - actual). Significance test encoding is for Mann-Whitney U or Spearman’s ρ where `**' indicates 0.001 < P < 0.01. Box plots show median and first and third quartiles with outliers as 1.5 times inter-quartile range (IQR).