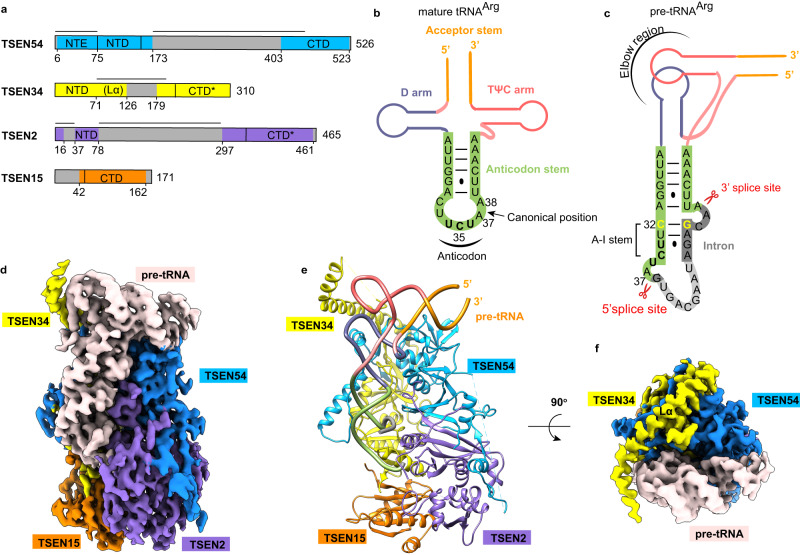
Fig. 1. Overall structure of the wild-type human TSEN–pre-tRNAArg complex.
a Domain organizations of human TSEN54, TSEN34, TSEN2, and TSEN15. Domains having structural information from this study are shown as colored domains. Disordered segments are shown in gray, and catalytic domains are labeled with a ‘*’ (star). The black lines represent the novel insertions in the human TSEN subunits as compared to the archaeal endonuclease. NTE, N-terminal extension; NTD, N-terminal domain; CTD, C-terminal domain; Lα, long α helix. b Schematic drawing of the secondary structure of mature tRNAArg from humans. Key regions of the tRNA are labeled. The anticodon is highlighted in bold. The intron insertion position is indicated by the black arrow. c Schematic representation of the folding of the pre-tRNAArg used in this study, with the same color scheme as in panel (b). The anticodon domain sequence is shown in green, and the intron in gray. The region in light gray is not observed in this study. The anticodon-intron (A-I) base pair is in yellow. The Watson-Crick base pairs are indicated with lines, and the G-U wobble is indicated by a dot. The A-I stem, the 3′ and 5′ splice sites are labeled. Elbow region is formed by the interactions between the D-loop and T-loop. d–f Cryo-EM reconstruction at 3.19 Å resolution and an atomic model of human TSEN–pre-tRNAArg complex. The pre-RNA is colored in misty rose (d, f) or as in panel c (e). The Cryo-EM map in panel (f) is viewed after a 90° rotation around the horizontal axis. The position of Lα is labeled. Structure figures are produced with Chimera42 and ChimeraX47.