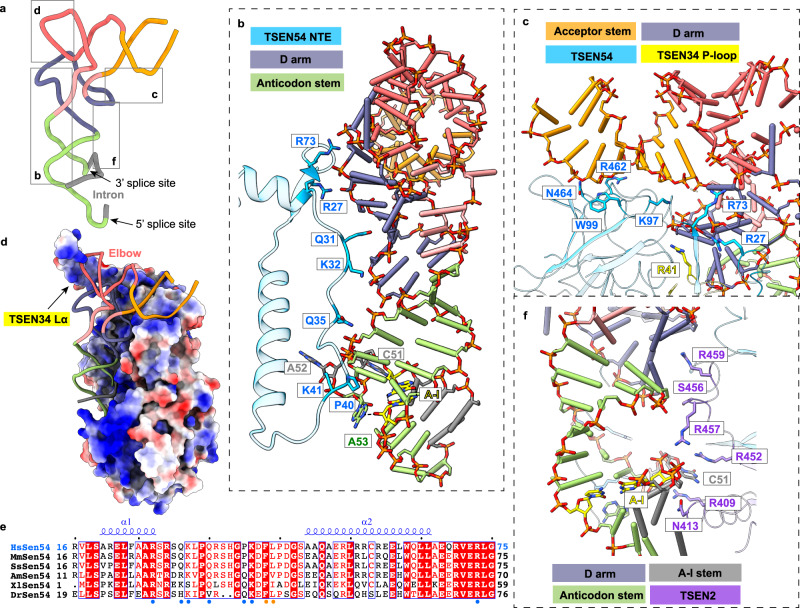
Fig. 3. Recognition of the mature body of pre-tRNA.
a The 3D structure of pre-tRNAArg. The color scheme is the same as in Fig. 1c. Close-up views depicting the interactions between pre-tRNA and proteins are shown in panels (b–d) and (f). b Detail view of D arm and anticodon stem recognition by the NTE of TSEN54. Regions (residues 20–75) of TSEN54 NTE are displayed. Key residues that are involved in recognition are shown as sticks. The nucleobases in the A-I base pair (yellow) and the 3′ bugle (green and gray) are shown as sticks. The last bulge nucleotide, A53, forms hydrogen-bonding interaction with the A-I base pair. c Recognition of the acceptor stem by TSEN54. R41 from P-loop of TSEN34 is also indicated. d Electrostatic surface of the TSEN complex, showing charged interface with the pre-tRNA. The positions of the elbow region and TSEN34 Lα are labeled. e Sequence alignment of the N-terminal insertion of selected vertebrate TSEN54 homologs. The secondary structure elements in the human TSEN54 structure are shown. Strictly conserved residues are marked in white with a red background, and well-conserved residues in red. The region that interacts with pre-tRNA is indicated in blue dots, and that with TSEN15 in orange dots. Hs: human; Mm: mouse; Ss: pig; Am: alligator; Xl: frog; Dr: zebrafish. f Interfaces between TSEN2 and pre-tRNA.