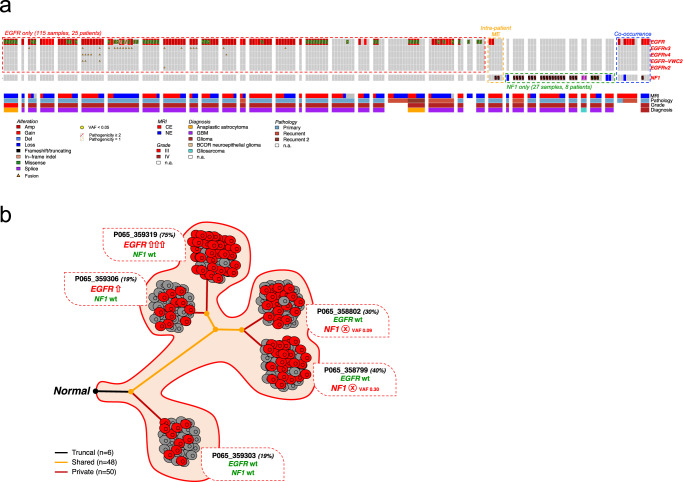
Fig. 4. Mutual genetic alteration profiles of EGFR and NF1 in IDH wild-type glioma.
a EGFR and NF1 somatic genetic alterations occurring in multiregional samples from IDH wild-type glioma. Samples are grouped by patient and clinical annotations are indicated in the bottom tracks. EGFR (red box) and NF1 (green box) alterations are mutually exclusive in 98.7% samples (152 out of 154, two-sided Fisher’s Exact test p = 1.72e−07). The mutual exclusivity between EGFR and NF1 alterations was also observed within the same patient (orange box). Co-occurring genetic alterations have been identified only in 2 samples from 2 patients (blue box). b Evolutionary model of glioblastoma from patient P065 that included 5 contrast-enhancing samples harboring mutual exclusive EGFR and NF1 alterations. NF1 truncating mutation specifically occurred in two samples with wild-type EGFR locus; conversely, EGFR was amplified in the other two NF1 wild-type samples. Tumor purity is indicated for each sample (percentages displayed). VAF, variant allele frequency. Number of truncal, shared, and private alterations are indicated.