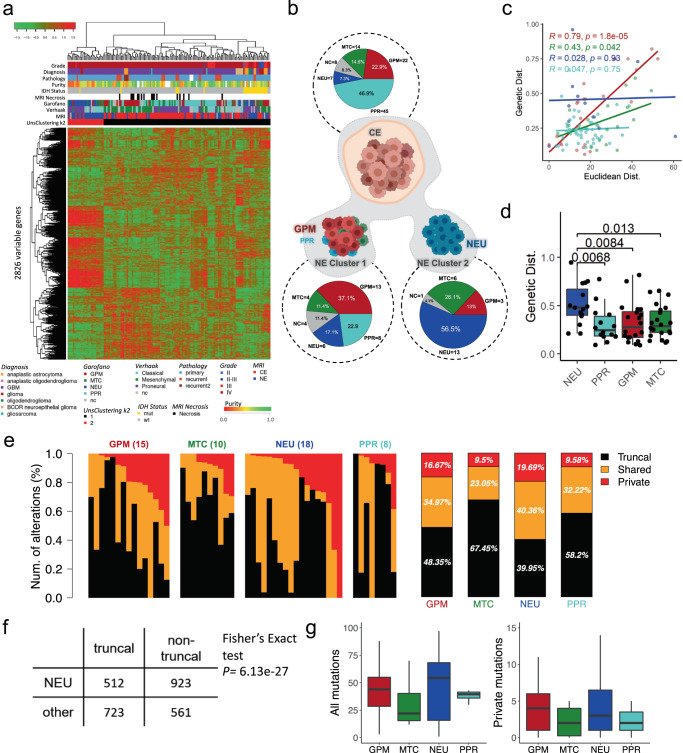
Fig. 7. Conventional MRI, transcriptomic, and genotypic characterization of NE region phenotypes.
a Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the 158 multiregional glioma samples; rows are the 2826 most variable genes. b Pie charts show the frequencies of pathway-based classifications of MRI CE samples (top) and MRI NE samples of unsupervised cluster 1 and 2, respectively (bottom). c Correlations between the genotypic and euclidean distance of paired samples with the same pathway-based classification. d Genetic distance of CE samples to NE samples of each pathway-based classification (n = 94 biopsy samples). Boxplots represent data minimum, 25th percentile, 50th percentile, 75th percentile, and maximum. The p-values are indicated above each comparison in the figure. e Private, shared, and truncal alterations in individual samples in the NE region classified as each pathway-based subtype (from left to right: glycolytic/plurimetabolic, mitochondrial, neuronal, and proliferative/progenitor), with the average of private, shared, and truncal mutations for each pathway-based classification displayed to the right. f The proportion of truncal mutations vs. non-truncal (private and shared) mutations in samples of NEU subtype was significantly different than the proportion of truncal mutations vs. non-truncal mutations in the other subtypes (one-tailed Fisher’s exact test p = 6.13e−27). g Box and whisker plots show the absolute number of total (left) and private (right) mutations in each pathway-based classification and the distribution of mutational burden across samples (n = 51 biopsy samples). Boxplots represent data 25th percentile, 50th percentile, and 75th percentile. The upper whisker extends from the upper hinge to the largest value no further than 1.5X IQR (inter-quartile range, or distance between the first and third quartiles) and the lower whisker extends from the lower hinge to the smallest value at most 1.5X IQR. c, d, e, g Source data are provided as a Source data file.