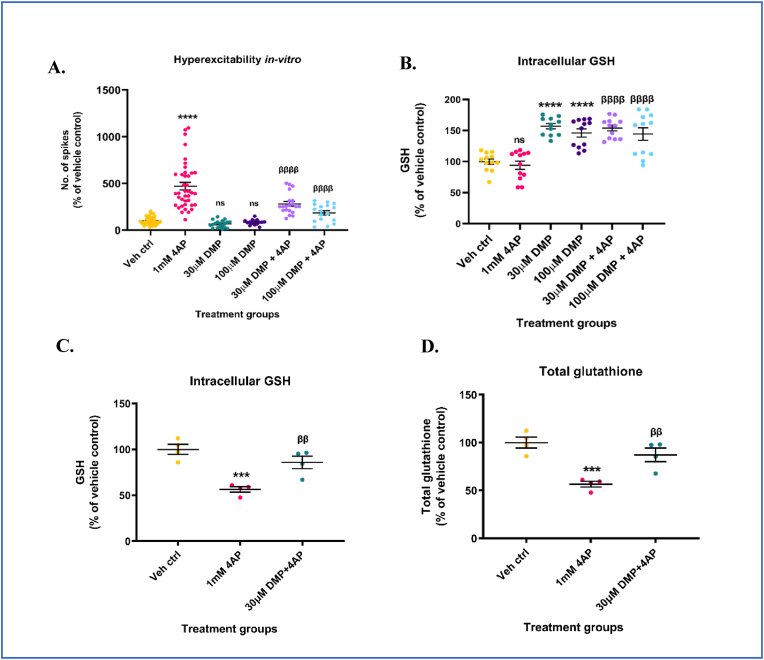
Fig. 1.
Dimercaprol (DMP) elevates intracellular GSH levels and protects against 4-aminopyridine (4AP)-induced neuronal hyperexcitability and GSH depletion. Primary neuronal-glial cerebrocortical cultures were pretreated with either 30 μM or 100 μM dimercaprol for 4 h followed by 1 mM 4AP stimulation for 1 h following which extracellular action potentials (number of spikes), and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels were measured. (A) Number of spikes measured on MEA system (B) GSH levels measured by HPLC. Primary neuronal-glial cerebrocortical cultures were treated with 30 μM DMP for 4 h followed by 1 mM 4AP treatment for 20 h. GSH and GSSG levels were measured by HPLC after the 24 h treatment paradigm. (C) GSH levels, and (D) Total glutathione (GSH+(2*GSSG)) levels. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (error bars). ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns: not significant versus vehicle control, ββp<0.01, ββββp<0.0001 versus 1 mM 4AP by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test. n = 7–8/grp (A), n = 2–4/grp (B, C, and D). N = 3–4 experimental replicates. Mean ± SD of raw data values of GSH normalized to total protein (nmol/mg protein) are stated in parentheses (GSH): a) Veh ctrl (13.6 ± 7.4); b) 1 mM 4AP (11.9 ± 4.1); c) 30 μM DMP (20.9 ± 10.7); d) 100 μM DMP (19.7 ± 9.6); e) 30 μM DMP+4AP (20.9 ± 10.2); and f) 100 μM DMP+4AP (19.4 ± 9.8) (1B); Mean ± SD of raw data values of GSH and total glutathione normalized to total protein (nmol/mg protein) are stated in parentheses (GSH; total glutathione) for each treatment group: a) Veh ctrl (23.66 ± 2.63; 23.76 ± 2.68); 1 mM 4AP (13.35 ± 1.43; 13.44 ± 1.42); 30 μM DMP+1 mM 4AP (20.29 ± 3.22; 20.71 ± 3.38) (1C and 1D).