Fig. 3.
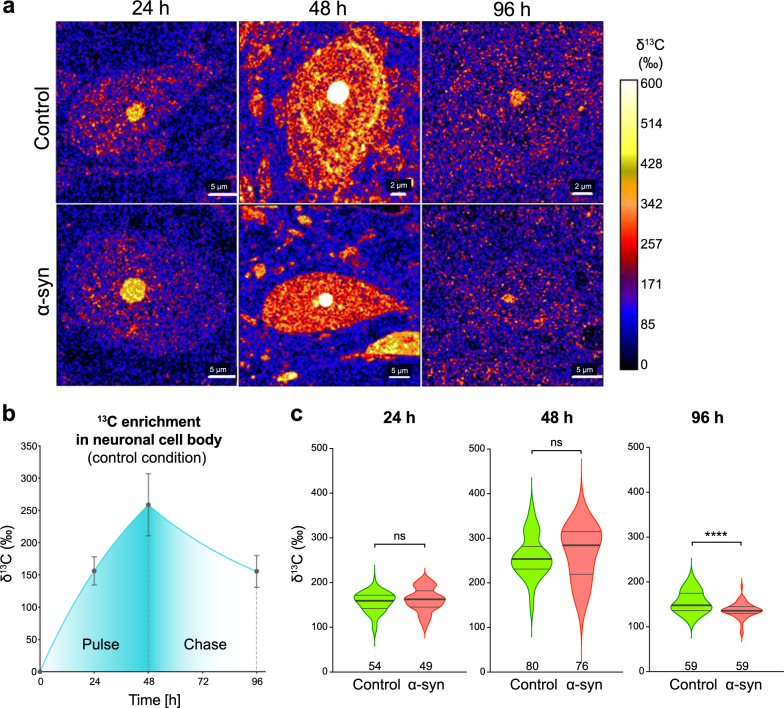
Kinetics of 13C incorporation in neuronal cell bodies in the substantia nigra pars compacta. a Representative maps of 13C isotope enrichment throughout pulse-chase experiment in neurons located in the SNpc, either in the control or AAV6-α-syn-injected SNpc. Scale bars: 2 and 5 µm. b Pulse-chase experiment: quantification of 13C enrichment in the whole cell body of nigral neurons in the SNpc injected with the non-coding control vector. Pulse phase: 13C enrichment at 24 h and 48 h after starting 13C-labeled glucose administration in the drinking water. The graph shows curve fitting with exponential plateau. Chase phase: an additional measurement was performed at 96 h and curve fitting was based on the assumption that the observed drop in 13C-enrichment follows a one-phase exponential decay. Data represent mean ± SD. c Violin plots showing 13C enrichment in the whole cell body. The graphs compare nigral neurons located in the SNpc injected with a non-coding AAV6 vector to their counterparts in the contralateral AAV6-α-syn-injected SNpc. The pulse-chase experiment was performed 30 days after intranigral vector injection. Note the effects of human α-syn overexpression on carbon turnover in the neuronal cell bodies during the chase period. The thick lines in the violin plots represent the median and the thin lines the upper and lower quartiles. The number of neurons analyzed is indicated at the bottom of the histogram bar. 24 h: N = 3 animals per group; 48 h: N = 4 animals per group; 96 h: N = 3 animals per group. Statistical analysis: multiple Mann–Whitney tests with False Discovery Rate (FDR) approach; ns = not significant; **** FDR-adjusted P < 0.0001