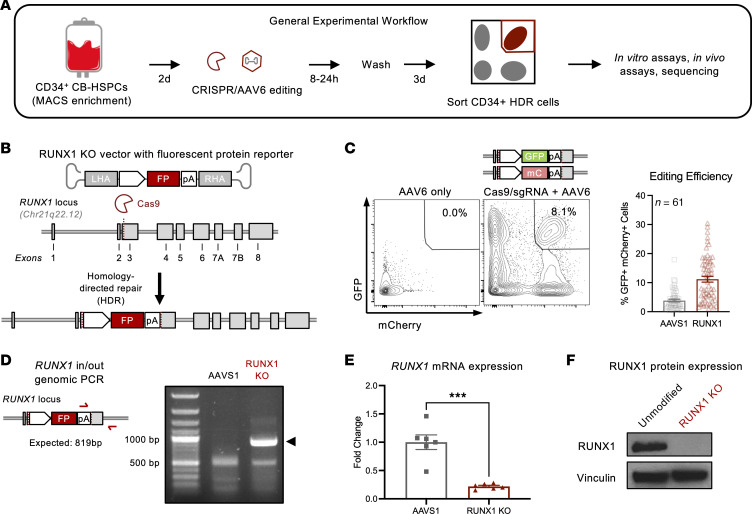
Figure 1. Targeting the endogenous RUNX1 locus in human HSPCs using CRISPR and homology directed repair.
(A) Umbilical CB is enriched for CD34 using magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS) and expanded in serum-free media with SCF, TPO, FLT3L, IL-6, and UM-171. After 2 days, cells are nucleofected with RUNX1- or AAVS1- targeting sgRNA-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein and exposed to AAV6 carrying donor DNA for 8 hours. Three days after editing, CD34+mCherry+GFP+ cells are sorted and plated for in vitro and in vivo assays or molecular profiling. (B) Recombinant AAV6 vector carries arms of homology flanking fluorescent reporter (FP) transgenes encoding GFP or mCherry as donor DNA for HDR at DNA double-stranded breaks generated by RUNX1-targeting sgRNA-Cas9. LHA, left homology arm; RHA, right homology arm; pA, poly-A. (C) Left: Biallelic modified GFP+mCherry+ double-positive cells are not present in controls lacking sgRNA-Cas9. mC, mCherry. Right: Quantification of double-positive HDR editing efficiency at the AAVS1 safe harbor locus and RUNX1 locus in CD34+ HSPCs. n = 61 CB donors. (D) Left: Schematic of in/out PCR spanning target-donor junction to confirm integration of the RUNX1-KO vector in the endogenous RUNX1 locus. Right: Agarose gel showing in/out PCR product in RUNX1-KO CD34+ HSPCs. (E) qPCR detection of fold change in RUNX1 expression relative to AAVS1 control and normalized to HPRT1. Unpaired t test: *** P < 0.001. n = 2 CB donors, 3 replicates. (F) Western blot of RUNX1 protein in unmodified and RUNX1-KO CD34+ HSPCs.