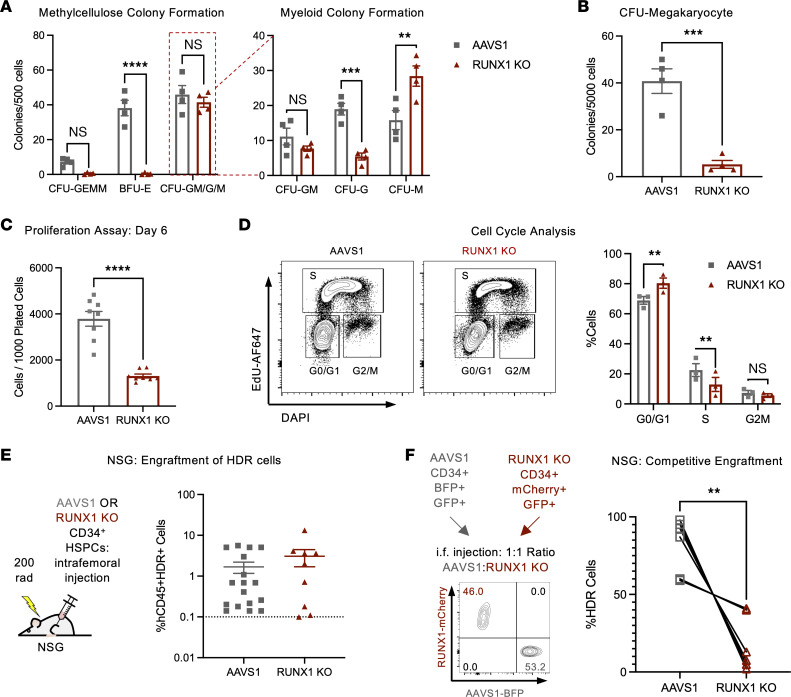
Figure 2. RUNX1 loss in human HSPCs causes hematopoietic and stem cell defects.
(A) CD34+ HDR HSPCs were plated in methylcellulose-based colony-forming assays and assessed for colony formation at 14 days. n = 4 CB. Two-Way ANOVA, Šidák’s multiple-comparison test: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (B) CD34+ HDR HSPCs were plated in collagen-based megakaryocyte colony-forming assays, and colonies were quantified after 10 days. n = 4 CB. Paired t test: ***P < 0.001. (C) CD34+ HDR HSPCs were plated in stem retention media (serum-free media with SCF, TPO, and FLT3L) and analyzed by flow cytometry for cell count at days 6. n = 8 CB donors. Paired t test: ****P < 0.0001. BFU, burst-forming units. GEMM, granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte. (D) CD34+ HDR HSPCs were incubated with EdU for 2 hours, stained with DAPI, and evaluated for cell-cycle status. n = 3 CB. Two-way ANOVA, Šidák’s multiple-comparison test: **P < 0.01. (E) CD34+ HDR HSPCs were injected intrafemorally into sublethally irradiated NSG mice, and human CD45+ HDR+ engraftment was evaluated upon sacrifice (at 24–26 weeks after transplantation). Unpaired t test NS (not significant). n = 5 CB donors, 9–18 mice. (F) BFP+ AAVS1 and mCherry+ RUNX1-KO cells were injected intrafemorally at a 1:1 ratio into NSG mice, and relative engraftment within the human CD45+ compartment was evaluated 18 weeks after transplantation. The FACS plot indicates representative ratio upon injection. The graph shows relative engraftment at 18 weeks; paired t test: **P < 0.01. n = 3 CB donors, 6 mice.