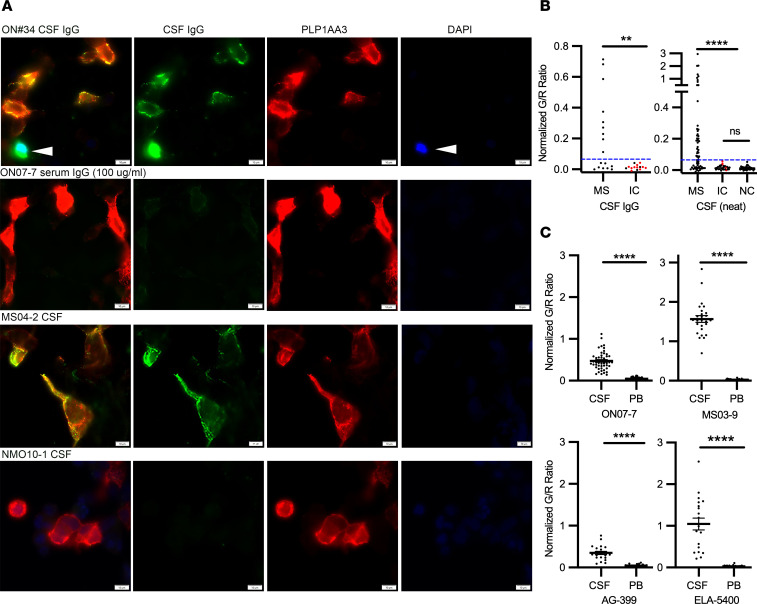
Figure 9. Detection of conformational PLP1-specific Abs in MS and control CSF.
(A) PLP1 and human IgG immunofluorescence on live PLP1-transfected HEKPE7 and cholesterol-treated cells 24 hours after transfection using CSF IgG (100 µg/ml), CSF neat, or serum IgG from MS or inflammatory control patients. Following cholesterol treatment, live-cell cultures were treated with DAPI (arrowheads) to identify dead cells. Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) Normalized and background-corrected mean ratios of green/red immunofluorescence signal (G/R) to single or small clusters of PLP1-transfected cells are shown for cohorts of clinically definite MS (n = 79), infectious (red circles) and noninfectious inflammatory neurologic controls (IC, n = 45), and noninflammatory neurologic controls (NC, n = 39) using either purified CSF IgG or CSF neat. Blue dashed lines indicate values 3 SDs above the mean of IC binding and distinguished positive from negative PLP1 binding. No significant differences in the mean G/R ratio were observed in the populations comprising IC CSF IgG (G/R = 0.015 ± 0.015), IC CSF (G/R = 0.016 ± 0.013) and noninflammatory neurologic controls (G/R = 0.013 ± 011). Fisher’s exact test was used to compare distributions between MS and control patients for each cohort; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. (C) Normalized ratios of green/red immunofluorescence signal (G/R) for PLP1-transfected cells incubated with the same IgG concentrations of serum or CSF from 4 PLP1+ MS patients. The ratio of mean CSF and serum-binding titers were greater than 8.2 for each patient, indicative of intrathecal synthesis of PLP1 complex–specific Abs. Statistical comparisons of replicate measurements from 2 to 3 independent transfections were made using Welch’s t test. ****P < 0.0001. Data are represented as means and SD.