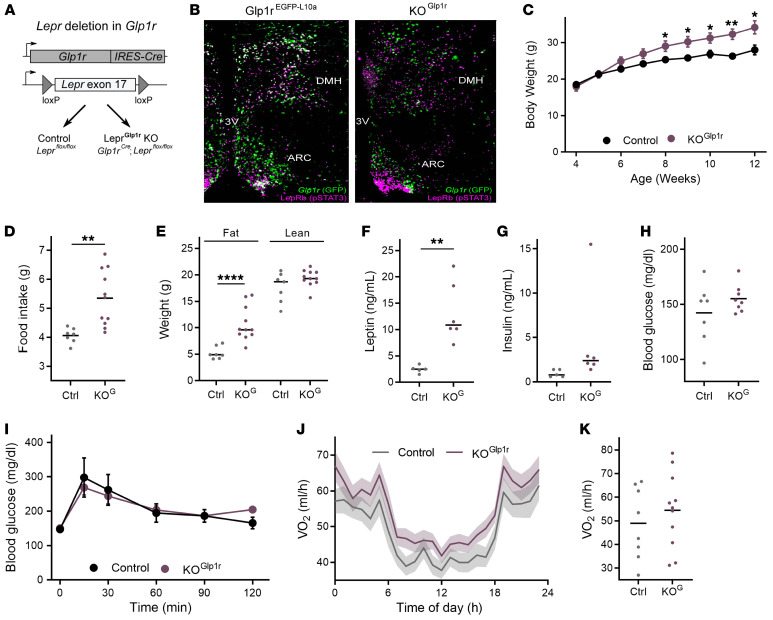
Figure 3. Requirement for Lepr in LepRbGlp1r neurons for the control of food intake and body weight by leptin in male mice.
(A) Experimental design showing the generations of Glp1rCre;Leprfl/fl (KOGlp1r or KOG) and Leprfl/fl control animals. (B) Representative images showing leptin-induced pSTAT-IR (LepRb, magenta) and GFP-IR (Glp1r, green) in Glp1rEGFP-L10a (left) and KOGlp1r (right) mice. Original magnification, ×4. (C–H) Body weight (C; n = 7 Ctrl, n = 11 KOGlp1r), food intake (D; n = 7 Ctrl, n = 11 KOGlp1r), body composition (E; n = 7 Ctrl, n = 11 KOGlp1r), serum leptin (F; n = 5 Ctrl, n = 6 KOGlp1r), serum insulin (G; n = 5 Ctrl, n = 6 KOGlp1r), and blood glucose (H; n = 7 Ctrl, n = 11 KOGlp1r) in control (black/gray) and KOGlp1r (purple) male mice. (I) Glycemic response to an i.p. glucose tolerance test in control (black; n = 7) and KOGlp1r (purple; n = 11) male mice. (J and K) VO2 measured in metabolic cages across the diurnal cycle (J) and averaged over 24 hours (K) for KOGlp1r mice (n = 11) and control (n = 8) male mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 by Student’s t test.