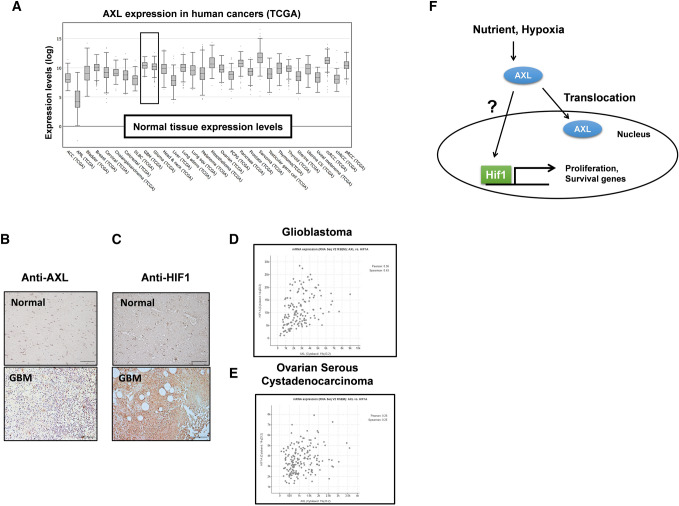
Fig. 5.
The expression of AXL and HIF-1α in human glioma. a Human AXL expression in different tumor types from the TCGA database.
Adapted from cBioPortal: http://www.cbioportal.org/index.do. b Human glioma tissue arrays were immuno-histochemically analyzed in terms of AXL staining. Representative images from samples from two patients are shown. Scale bars: 100 μm. c Human glioma tissue arrays were immunohistochemically analyzed in terms of HIF-1α staining. Representative images from samples from two patients are shown. Scale bars: 100 μm. d the co-expression of AXL mRNA and HIF-1α mRNA from 142 queried glioblastoma (GBM) samples in the TCGA database. e The co-expression of AXL mRNA and HIF-1α mRNA from 182 ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma queried samples. Adapted from cBioPortal: http://www.cbioportal.org /index.do. f The working model of the role of AXL in GBM survival. Under the control of the tumor microenvironment, such as the nutrient supply and hypoxia conditions, AXL translocates to the nucleus. The inhibition of HIF-1α degradation and the nuclear trans-localization of HIF-1α by hypoxia trigger the expression of AXL. Nuclear HIF-1α promotes the proliferation and survival genes in GBM