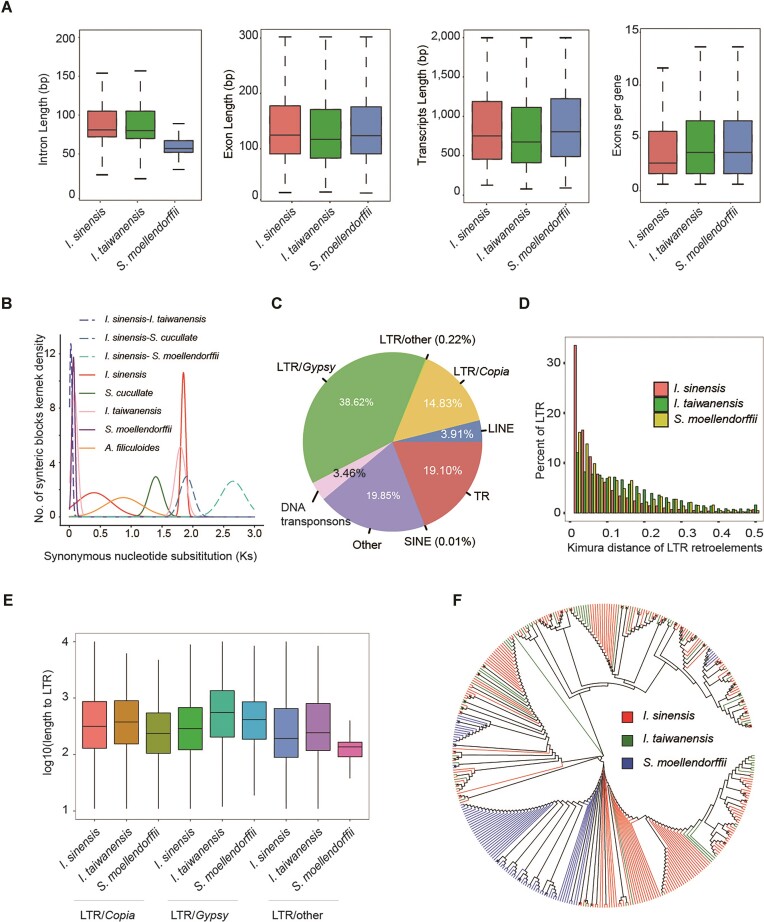
Figure 2:
Genomic features of the I. sinensis genome. (A) Boxplot showing intron, exon, and transcript length comparisons among the genomes of I. sinensis, I. taiwanensis, and S. moellendorffii. Boxes indicate the first quartile, median, and third quartile with whiskers extending up to 1.5 times the interquartile distance. (B) Frequency distribution of Ks based on the distribution of substitution rates of paralogs in 3 lycophytes (I. sinensis, I. taiwanensis, S. moellendorffii) and 2 ferns (A. filiculoides and S. cucullata). The two Ks peaks (0.4 and 1.8) indicate 2 WGDs in I. sinensis. (C) Pie chart illustrating of the major classes of repetitive DNA in I. sinensis. LINE, long interspersed nuclear element; LTR, long terminal repeat; SINE, short interspersed transposable element; TR, tandem repeat. (D) The relative ages of LTR retroelements computed as Kimura distances suggest a long period of retroelement transposition activity. (E) Boxplot showing distributions of LTR family lengths in I. sinensis, I. taiwanensis, and S. moellendorffii. (F) Maximum likelihood phylogeny analysis of Gypsy retroelements showing the expansion of Gypsy in I. sinensis and I. taiwanensis.