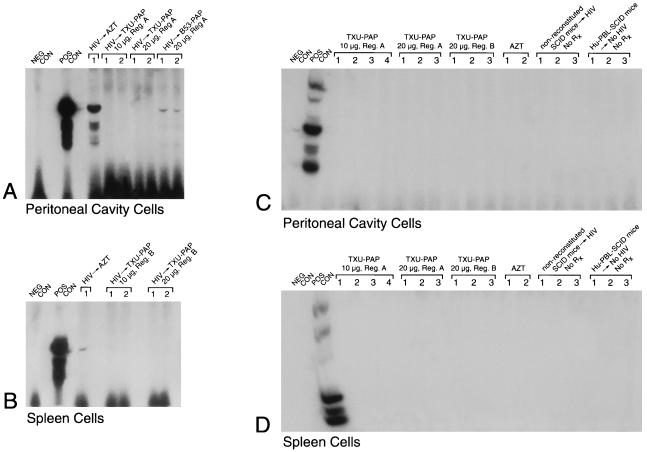
FIG. 2.
In vivo anti-HIV-1 activity of TXU (anti-CD7)-PAP. Hu-PBL-SCID mice were inoculated with clinical HIV-1 isolates in a biosafety level 3 containment facility as described in Materials and Methods. PAP immunoconjugates were administered intraperitoneally by injecting half of the total dose as an intraperitoneal bolus dose and delivering the remainder of the total dose over 2 weeks with Alzet micro-osmotic pumps (regimen A) or by administering the total dose by daily intraperitoneal injections over a 5-day treatment period (regimen B). In the AZT-treated mice, AZT was added to their water at a final concentration of 1 mg/ml, resulting in an average consumption of 200 mg of AZT per kg/day. All treatments were initiated immediately prior to the inoculation of HIV-1. Two weeks after infection with HIV-1, Hu-PBL-SCID mice were electively killed and their peritoneal lavage cells as well as spleen cells were examined for evidence of infection by a culture assay for HIV-1 (Table 1) as well as by PCR amplification of a 115-bp DNA sequence in the gag region of the HIV-1 genome. Polyacrylamide gels of the PCR-amplified HIV-1 DNA hybridized with the 32P-labeled SK19 probe are shown. No PCR evidence of HIV-1 infection was found in any of the TXU-PAP-treated mice. The controls included (i) the PCR buffer without the genomic DNA (NEG CON), (ii) PCR product of DNA from HIV-1-injected but unreconstituted SCID mice as well as from uninfected Hu-PBL-SCID mice as negative background controls, and (iii) HIV-1 control plasmid DNA (POS CON) (Perkin-Elmer Cetus) as well as DNA from infected but untreated (data not shown) Hu-PBL SCID mice as positive DNA controls. (A and C). Data for PCR detection of HIV in peritoneal cavity cells. (B and D). Data for PCR detection of HIV in spleen cells. Rx, treatment. Each lane corresponds to a Hu-PBL-SCID mouse sample or the indicated controls.