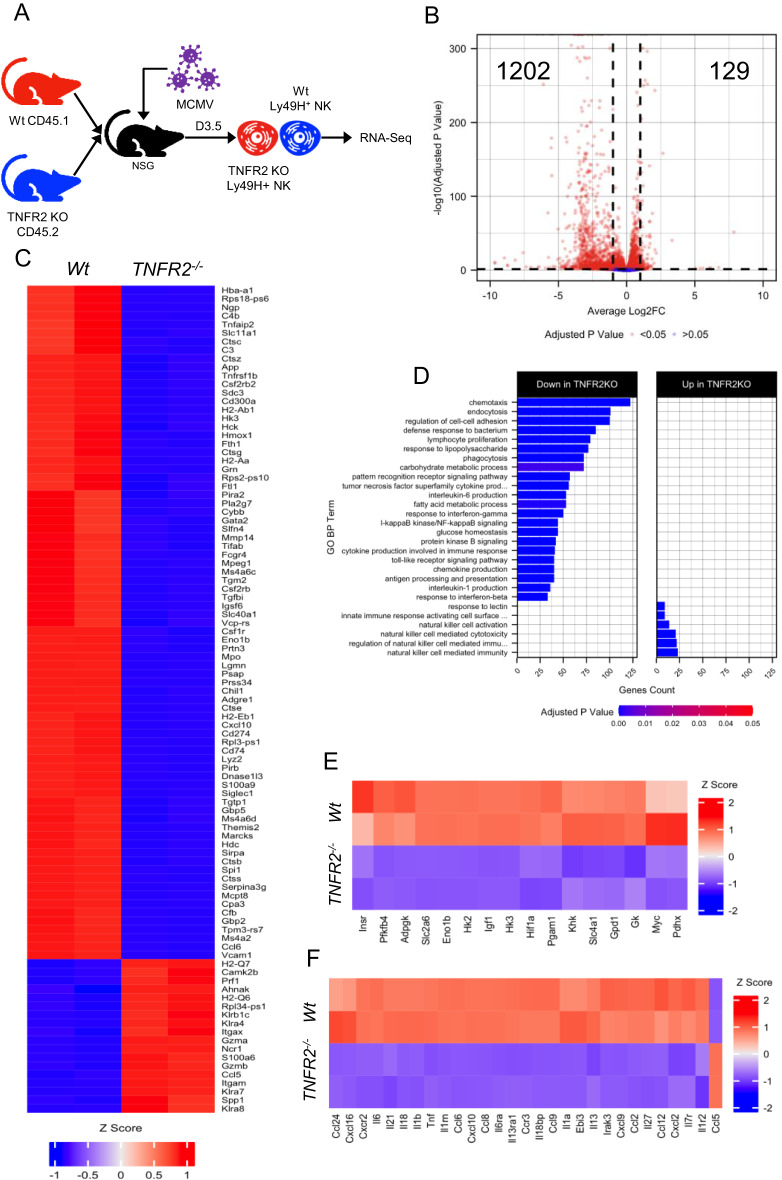
Fig. 7.
NK cells from TNFR2 KO mice displayed reduced expression levels of the genes associated with glycolytic metabolic programming following acute MCMV infection in vivo. A Purified NK cells from wild-type (CD45.1) and TNFR2 KO (CD45.2) mice were co-transferred into NSG mice. One day later, mice were intraperitoneally infected with MCMV. Mice were sacrificed on D3.5 following infection, and splenic Ly49H+CD45.1+ and Ly49H+CD45.2+ NK cells were sorted by flow cytometry and used for bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis. B Volcano plot depicting differentially expressed genes (adjusted p value < 0.05 and 1 log2-fold change cutoff) between wild-type and TNFR2 KO NK cells. C Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of the top 100 differentially expressed genes, ranked by adjusted p value. D Over-representation analysis of Gene Ontology Biological Process (GO BP) on significantly (adjusted p value < 0.05) differentially expressed genes with upregulated (log2-fold change > 0.5) and downregulated (log2-fold change < −0.5) expression in NK cells from wild-type and TNFR2 KO mice. Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of selected differentially expressed genes involved in aerobic glycolysis (E) and cytokines, chemokines, and their receptors (F) in NK cells from wild-type versus TNFR2 KO mice. Data are from one experiment performed in duplicate, and samples were isolated from the pooled spleen sample generated from three infected mice