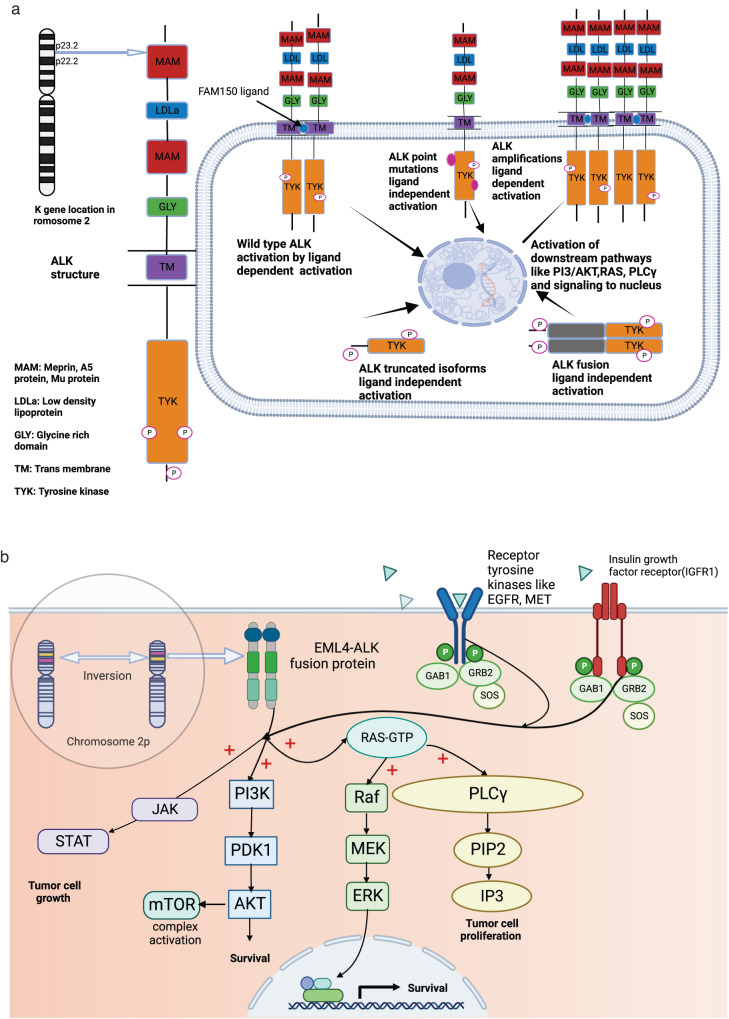
Fig. 1. Biology of ALK.
a ALK gene location, structure, and alterations. The ALK gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 2 (2p23). ALK receptor is a member of the insulin receptor superfamily and is a tyrosine kinase enzyme; its structure consists of the extracellular domain (two MAM, one LDLa), and one glycine-rich domain, a connecting transmembrane region, and an intracellular domain (tyrosine kinase domain). ALK receptors (CD246) are activated physiologically by FAM150 ligand binding followed by auto and transphosphorylation of residues, which promotes signaling to the nucleus. Intra tyrosine kinase (TYK) gain of function mutations can lead to ligand-independent downstream pathway activation. Amplified ALK gene sustains downstream signaling in a ligand-dependent manner. Similarly, truncated or isoform ALK gene that loses parts of its extracellular domain and ALK gene fusions can lead to downstream pathway activation, cell cycle progression, proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. b Formation of EML4-ALK4 fusions and activation of downstream pathways. The figure inside the bubble depicts a small inversion within short arm of chromosome 2p, which results in the formation of a fusion gene comprising portions of (EML4) and (ALK) genes. ALK fusion protein activates downstream signaling pathways, among them, the most relevant and characterized pathways are the (MAPK/ERK), the (JAK-STAT), the (PI3K– Akt), and the (PLCγ) pathways. ALK fusion proteins have a strong oncogenic potential, and it ultimately promotes tumor cell progression. IGF1R and other receptor tyrosine kinase such as EGFR and MET also interact with ALK and lead to activation of downstream pathways. Activation of EGFR and IGF1R sometimes leads to development of bypass resistance pathways. Abbreviations: Akt protein kinase B, ALK Anaplastic lymphoma kinase, EML4 echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, GAB1 growth factor receptor-bound 2 associated binder 1, GRB growth factor receptor-bound, GTP guanosine triphosphate, IP3 inositol triphosphates, JAK Janus kinase, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, PDK1 pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1, PI3K phosphoinositide 3 kinase, PIP2 phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PKC protein kinase C, PLC-γ phospholipase C γ, RAF rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma, RAS rat sarcoma virus gene, SOS son of sevenless gene, STAT signal transducer and activator of transcription. Created by Biorender.com.