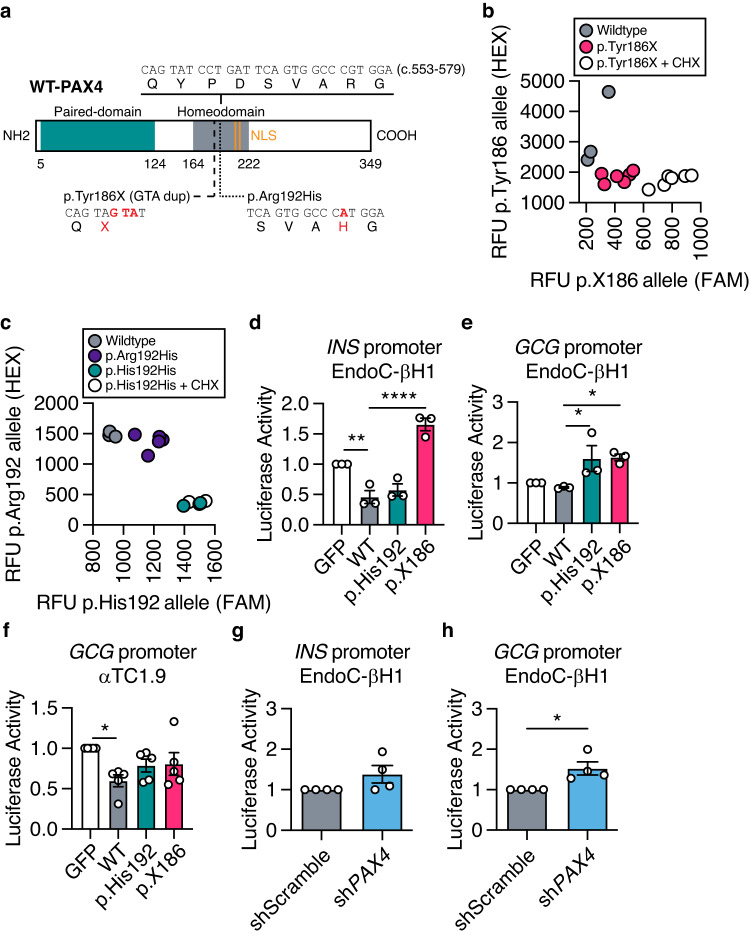
Fig. 5. Molecular function of PAX4 variants in human EndoC-βH1 cells.
a Illustration of human full-length wildtype (WT) PAX4 protein. Functional domains are depicted in green (paired-domain) and gray (homeodomain). Nuclear localization sequences (NLS; orange) are located at amino acids 206–210 and 212–216. Part of the homeodomain sequence that contains the PAX4 variants (c.553–579) and the amino acid changes of p.Tyr186X and p.Arg192His are highlighted. b Allele-specific qPCR of PAX4 transcript for p.Tyr186 and p.X186 alleles following cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. c Allele-specific qPCR of PAX4 transcript for p.Arg192 and p.His192 alleles following CHX treatment. d, e Luciferase activity of (d) INS and (e) GCG gene promoters in EndoC-βH1 cells overexpressing WT-PAX4, p.His192 and p.X186 (n = 3). f Luciferase activity of the GCG gene promoter in αTC1.9 cells overexpressing WT-PAX4, p.His192 and p.X186 (n = 5). g, h Luciferase activity of (g) INS and (h) GCG gene promoters in shScramble and shPAX4 EndoC-βH1 cells (n = 4). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by t test or two-way ANOVA. n > 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. Source data is provided in the Source Data File.