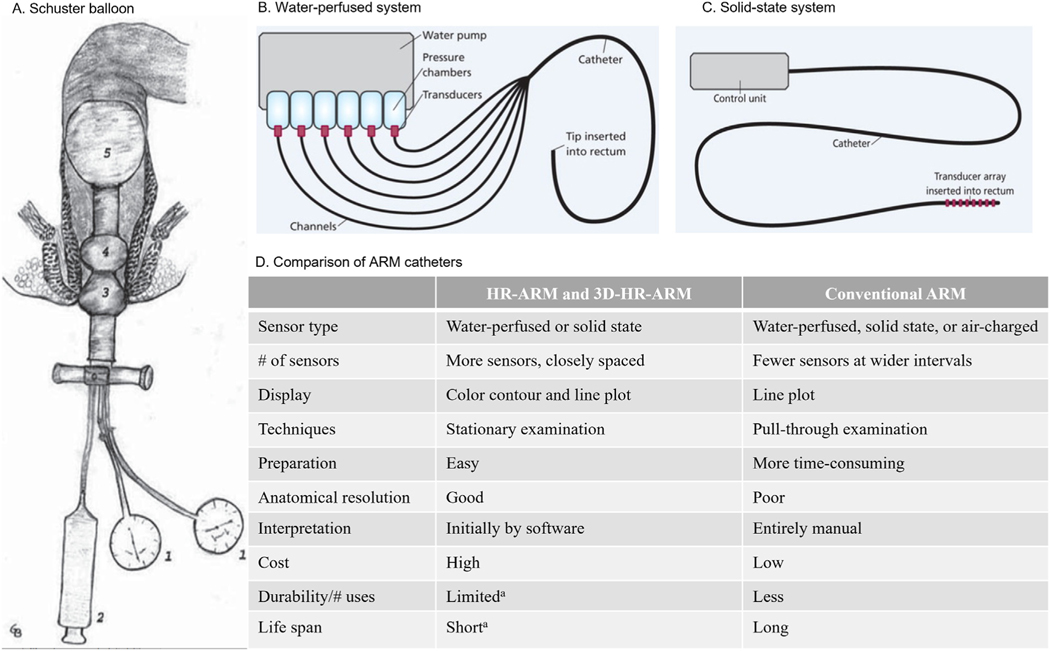
Figure 1.
ARM system descriptions. (A). Air-filled balloon of Schuster. 1, aneroid manometer; 2, syringe for air insufflations; 3, pear-shaped balloon (for the external anal sphincter); 4, doughnut-shaped balloon (for the internal anal sphincter); 5, rectal balloon for eliciting the rectoanal inhibitory reflex. Reprinted with permission from Pfeifer and Oliveira.28 (B). Water-perfused system. Reprinted with permission from Solanki D, Hibberts F, Williams AB. Pelvic floor investigations for bowel dysfunction (part 2): anorectal physiology (manometry). Gastrointest Nurs. 2019;17:24. (C). Solid-state system. Reprinted with permission from Solanki D, Hibberts F, Williams AB. Pelvic floor investigations for bowel dysfunction (part 2): anorectal physiology (manometry). Gastrointest Nurs. 2019;17:24. (D). Comparison of ARM catheters. Reprinted with permission from Bharucha et al.31 aFor high-resolution ARM (HR-ARM) catheters that use solid-state sensors. 3D, 3-dimensional.