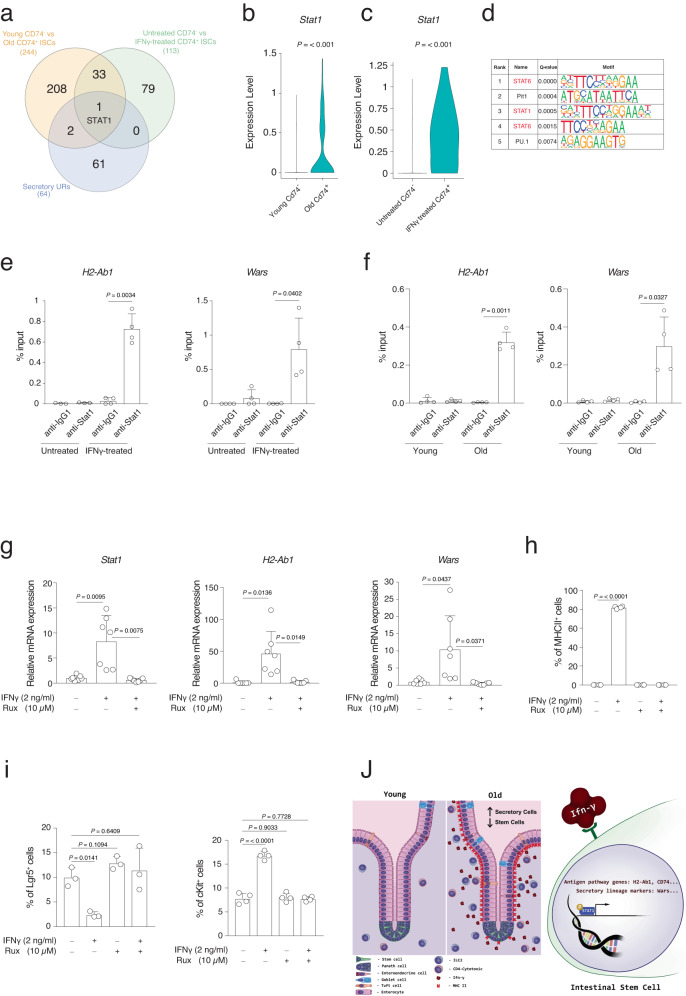
Fig. 7. Stat1 transcription factor mediates the IFNγ effect during aging.
a Gene set A: DEGs using young CD74− intestinal stem cell versus old CD74+ intestinal stem cell in crypts, Gene set B: DEGs using control CD74− intestinal stem cell versus IFNγ treated CD74+ intestinal stem cell in organoids, Gene set C: IPA-predicted upstream regulators for secretory lineage. b, c Box plot of Stat1 expression in the indicated groups. P value was calculated by two-tail Wilcoxon rank sum test. d Transcription factor and binding motif prediction on the promoters of the gene markers of the secretory cells in intestine. Top5 significant predicted motifs (q value < 0.001) are shown, indicating STAT6 and STAT1 were significantly enriched to bind secretory lineage gene promoters. P values was calculated by two-tail binomial distribution. Q value was Benjamini-adjusted p value. e, f ChIP-qRT-PCR analysis of the ChIP of Stat1 on H2-Ab1 and Wars promoters in e organoids treated or untreated with IFNγ (2 ng/ml) for 24 h or f intestinal crypts of young or old mice. Each dot represents one mouse. n = 4 mice per group were analyzed. Error bars represent the SD. P value was calculated by paired two-tail t test. g qRT-PCR analysis of Stat1, H2-Ab1, and Wars gene expression level in the indicated conditions. n = 7 mice per group were analyzed. Error bars represent the SD. P value was calculated by two-sided Welch’s t test. h The bar chart shows the percentage of MHCII+ cells in the indicated conditions. Organoids treated with IFNγ (2 ng/ml) with or without Ruxolitinib (Rux) for 3 days. n = 4 mice per group were analyzed. Error bars represent the SD. P value was calculated by two-sided Welch’s t test. i The bar chart shows the percentage of Lgr5+ cells and cKit+ cells in the indicated conditions. n = 4 mice per group were analyzed. Error bars represent the SD. P value was calculated by two-sided Welch’s t test. j Graphical abstract modeling aging-induced alteration in intestinal tissue.