Fig. 8.
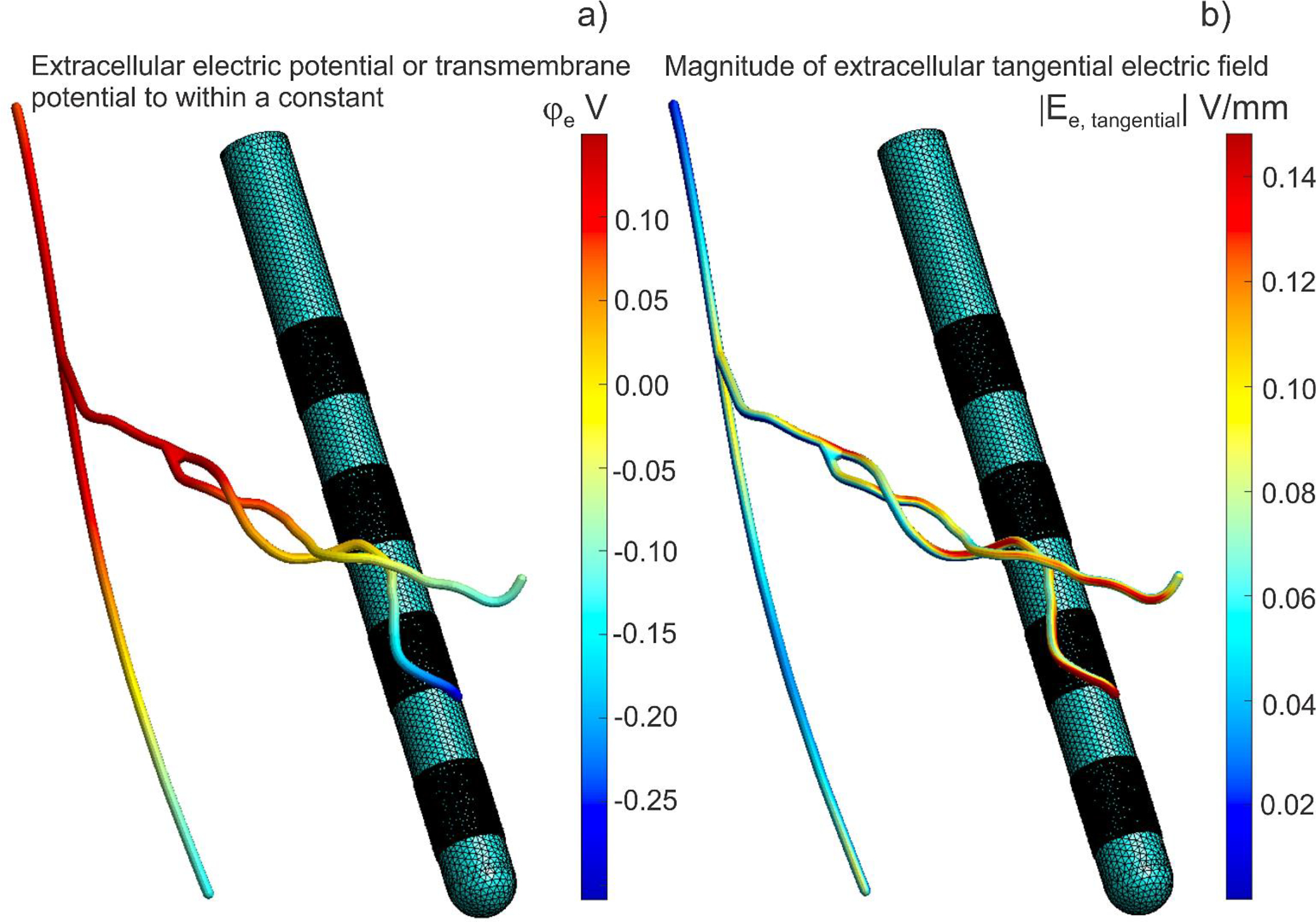
Computations for a 2 μm thick axon #1 were projected onto the corresponding tubular surface with a much larger diameter of 200 μm for visualization purposes only. Electrode 0 (bottom) is a cathode, electrode 3 (top) is an anode at 1 mA of the net current. a) Extracellular electric potential at the end of initial polarization for axon #1. The transmembrane potential is this value minus the axon resting potential. The transmembrane potential is simultaneously the double layer dipole density to within a multiplicative constant – the dielectric permittivity. b) Magnitude of extracellular electric field at the end of initial polarization for axon #1.
