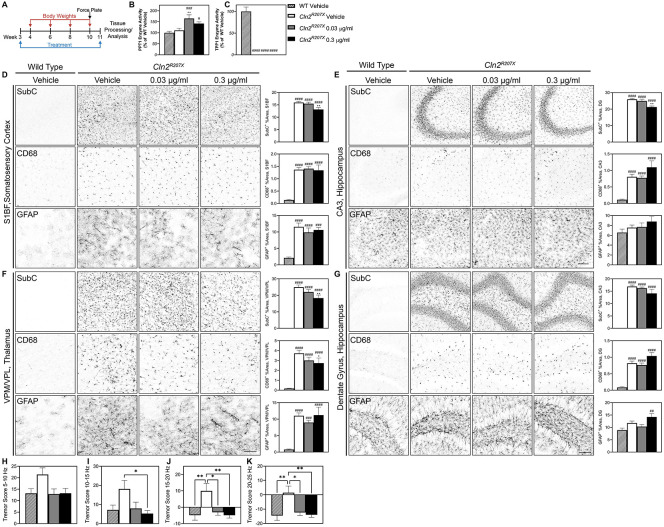
Figure 3. Short-term treatment with AF38469 improves histopathological and behavioral outcomes in Cln2R207X mice.
(A) Homozygous Cln2R207X and littermatewild type mice received continuous treatment with AF38469 or vehicle via drinking water starting at wean until 11 weeks of age. (B) Treatment with AF38469 (0.03 μg/ml) significantly increased PPT1 enzyme activity levels in Cln2R207X treated mice. (C) Treatment with AF38469 had no impact on TPP1 enzyme activity levels Cln2R207X treated mice. (D, E) AF38469 treatment (0.3 μg/ml) in Cln2R207X mice significantly prevented SubC accumulation and had no impact on microglial reactivity (CD68+) or astroglial activation (GFAP+) in the S1BF of the somatosensory cortex and CA3 of the hippocampus. (F) Treated Cln2R207X mice (0.3 μg/ml) saw significant prevention of accumulation of mitochondrial ATP synthase subunit C (SubC+) and reduction of microgliosis (CD68+) in the VPM/VPL of the thalamus with no impact on astrocytosis (GFAP+). (G) Treatment with AF38469 had no impact on CLN2 Batten disease pathology in the dentate gyrus and hilus regions of the hippocampus. (H-K) Tremor index scores were reduced and restored to wild type levels in AF38469 treated Cln2R207X mice when compared to vehicle treated mice. Mean ± S.E.M. (B-G) Nested one-way ANOVA with a Šidák post-hoc test (H-K) One-way ANOVA with a Šidák post-hoc test */#p<0.05, **/##p<0.01, ***/###p<0.001, ****/####p<0.0001. Hashsigns indicate comparison to WT, asterisks indicate comparison to mutant vehicle. Scale bar, 100 μm. n = 6-8 animals/treatment.