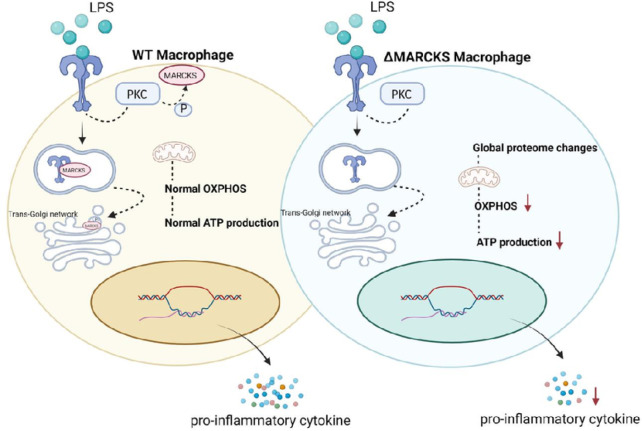
Figure 8. Hypothetical mechanism explaining the effect of LPS signaling in MARCKS deficient macrophages.
In response to the LPS signaling in macrophages, LPS binds to the TLR4 and the signaling cascade is initiated. In WT macrophages after LPS stimulation, PKC is activated and MARCKS is phosphorylated. Then, MARCKS migrates from the plasma membrane to the cytoplasm and can colocalize with TLR4 at an early endosome. Phospho-MARCKS also co-localizes with the trans-Golgi network where the TLR4 signal transduction is taking place resulting in the pro-inflammatory cytokine production. In contrast, MARCKS deficient macrophages induce global proteome changes resulting in decreased OXPHOS and the ATP production. The reduction of OXPHOS and the ATP production results in low energy status of the macrophages which may cause the lower cytokine secretion.