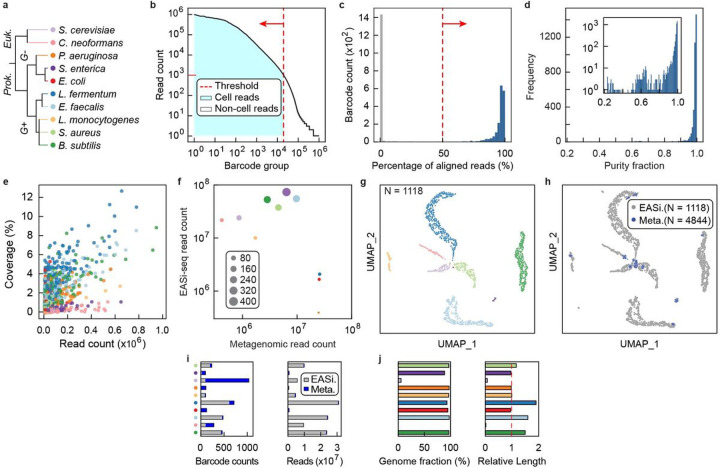
Figure 2. EASi-seq identifies single cells and has strain-level resolution.
a) The ZymoBIOMICS microbial synthetic community consisting of 10 species was analyzed by EASi-seq. Classification of each species is provided, with assigned colors used in the following panels.
b) Barcode rank plot of obtained data. Barcode groups were filtered by read counts, with less than 1000 reads used as the cutoff.
c) The barcode groups were further filtered by alignment rates to reference genomes. Barcode groups are mapped to the combined reference genomes of the 10 species, and barcode groups with an alignment rate of less than 50% were removed.
d) Purity distribution of barcode groups after data filtering, defined as the percentage of the reads mapping to the species most represented among read alignments. Inset shows purity distribution as a log-scale.
e) Coverages of each barcode group, color coded by species.
f) The comparison between metagenomic and single cell sequencing. Scatter plot shows the read counts of metagenomics sequencing data and combined EASi-seq barcode groups. Data points are color coded by species and their sizes are proportional to barcode counts after filtering.
g) UMAP clustering by Taxonomic discovery algorithm, color coded by species. Each barcode group is classified using a k-mer based taxonomy classifier (Kraken2). The output files were combined at the genus level. The barcodes were filtered by the percentage of mapped reads and taxonomical purity, which is the percentage of the dominant taxa. The vector of the genus abundance in each barcode was used to generate the UMAP and each barcode is annotated by the most abundant genus.
h) UMAP clustering shows the integration of the EASi-seq data (gray) and metagenomic data (blue). Each contig associated short read group in the assembled metagenome of the same sample was treated as a barcode and processed by the Taxonomic discovery algorithm.
i) Barcode counts and read counts in each UMAP cluster, grouped by batch (EASi-Seq or Metagenome assembly).
j) Evaluation of contigs assembled by grouping reads from all barcodes in each cluster. All the reads within a cluster were assembled into contigs using Spades and evaluated by Quast using the reference genome. Left, Genome coverage. Right, relative contig length normalized to reference genome.