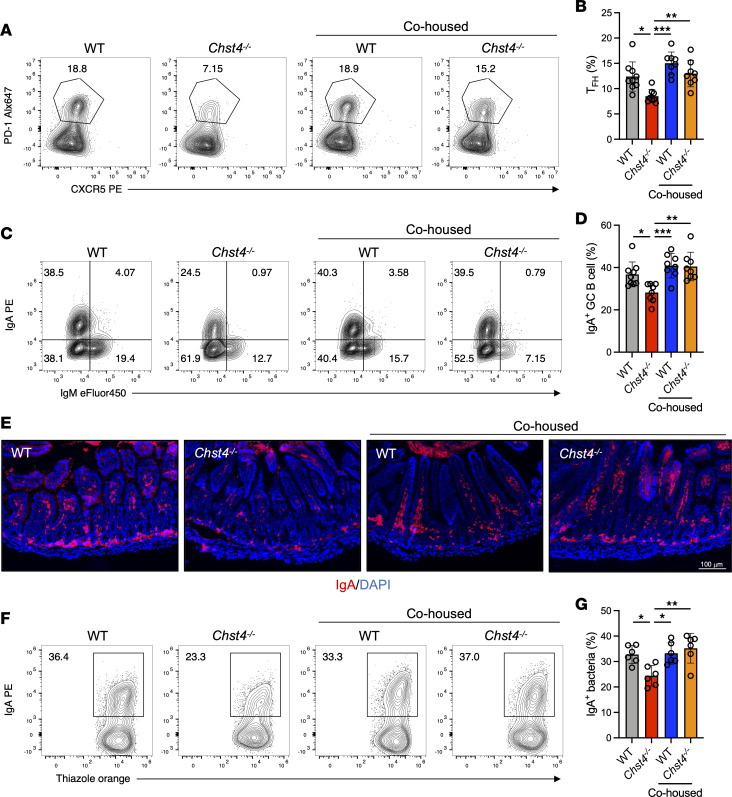
Figure 8. GlcNAc-6-O-sulfation on mucins enhances Tfh differentiation and IgA production via regulation of the gut microbiota.
(A) Representative flow cytometry plot of Tfh cells from WT and Chst4–/– mice after 3 weeks of cohousing. (B) Frequency of Tfh cells shown in A (WT n = 9, WT/cohoused n = 8, Chst4–/– n = 8, Chst4–/–/cohoused n = 8). (C) Representative flow cytometry plot of GC B cells from WT and Chst4–/– mice. (D) Frequency of GC B cells in C expressing IgA (WT n = 9, WT/cohoused n = 8, Chst4–/– n = 8, Chst4–/–/cohoused n = 8). (E) Immunofluorescent staining of IgA in small intestinal tissue. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Representative flow cytometry plot of IgA-binding bacteria from WT and Chst4–/– mice (n = 6). (G) Frequency of IgA-binding bacteria in F. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments, and presented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 via 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test.