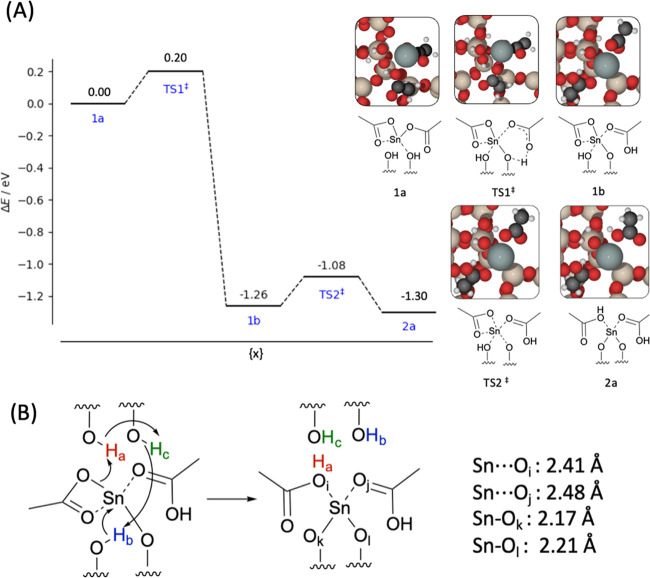
Figure 3.
(A) Relative energy (ΔE) profile for the transformation of acetate ligand from bidentate (Structure 1) to monodentate (Structure 2) via TS1, with acetic acid formed via the transfer of H from a silanol of the framework onto the acetate ligand. Energies are calculated using periodic DFT. Insets show the structures at each respective geometry. (B) Scheme showing the concerted movement of H during the reaction, resulting in rearrangement of the remaining silanol moieties and H transfer from the framework onto the acetate ligand to form Sn-bound acetic acid, where the resultant Sn–Ox distances are also noted. Red, beige, white, black, and gray atoms represent O, Si, H, C, and Sn, respectively.