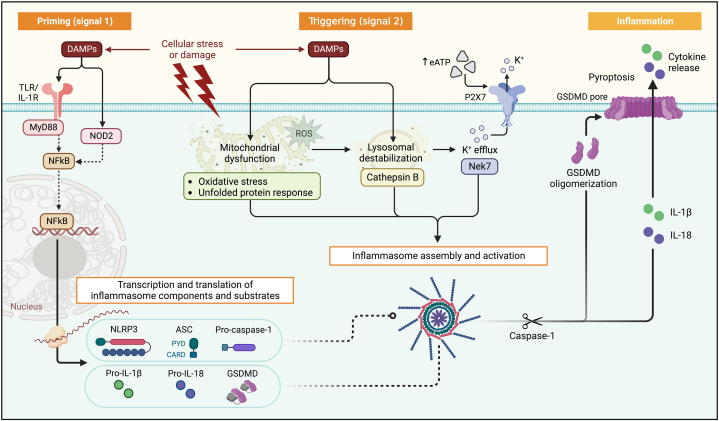
Figure 2.
Schematic of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
NLRP3 inflammasome activation requires 2 signals. Priming (signal 1) is induced by DAMPs, including the IL-1β/(pro)–IL-1α or extracellular ATP released during tissue injury. DAMPs activate membrane receptors, including TLRs and IL-1R, leading to NF-κB translocation into the nucleus, and transcription and translation of inflammasome components and the precursors of IL-1β and IL-18, which accumulate in the cytoplasm. Triggering (signal 2) induces inflammasome assembly and activation, promoted by extracellular ATP (through purinergic receptor P2X7R), or other intracellular other DAMPs (eg, mitochondrial or lysosomal proteins, like ROS and cathepsin B). These induce K+ efflux with NLRP3 activation. In response, NLRP3 oligomerizes and binds ASC and procaspase-1, resulting in autocatalytic activation of procaspase-1 to caspase-1. Caspase-1 cleaves pro–IL-1β and pro–IL-18 into their active forms. Caspase-1 also cleaves GSDMD, producing N-terminal fragments that oligomerize and form cell membrane pores, which enable extracellular release of IL-1β and IL-18. Caspase-1 and GSDMD pores also mediate pyroptotic cell death. Created with BioRender.com. ASC = apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; ATP = adenosine triphosphate; CARD = caspase recruitment domain; DAMPs = damage-associated molecular-patterns; GSDMD = gasdermin D; IL = interleukin; IL-1RA = interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; IL-1R = interleukin-1 receptor; MyD88 = myeloid differentiation factor 88; NLRP3 = NACHT-, LRR-, and pyrin domain–containing protein 3; NF-kB = nuclear factor-kappa B; NOD2 = nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2; P2X7R = P2X7 receptor.