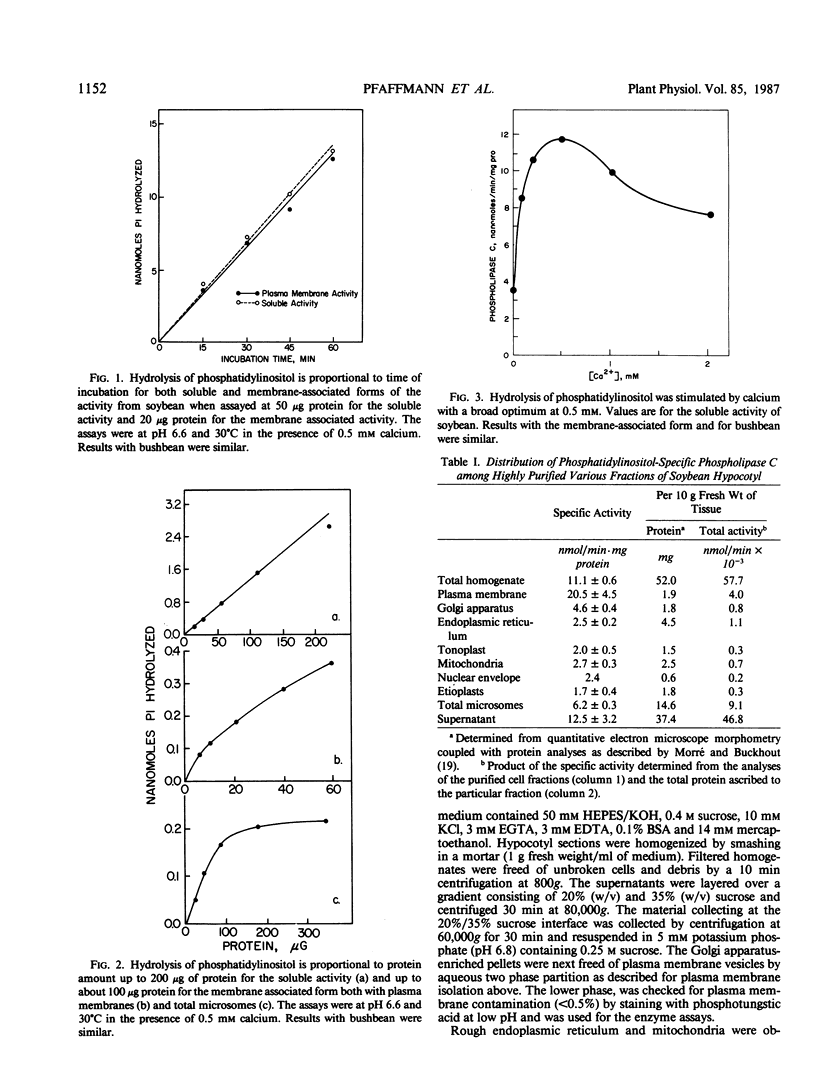
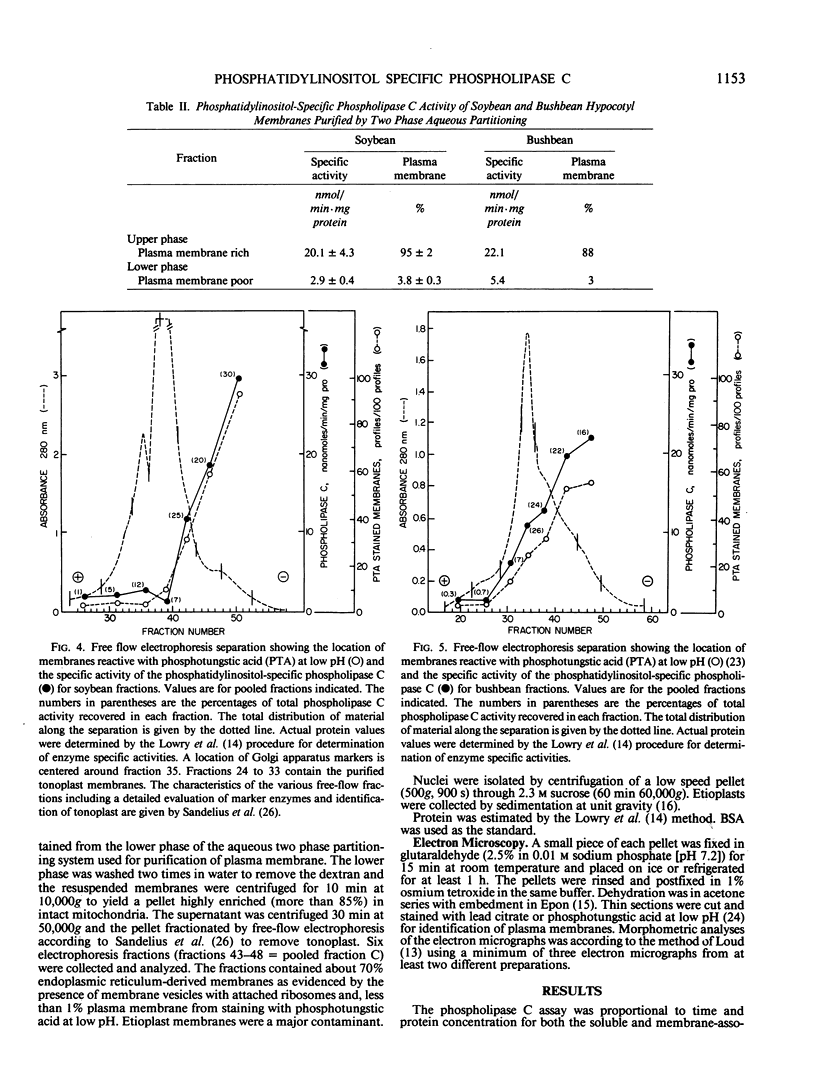
Abstract
A phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of plant stems (EC 3.1.4.10) assayed at pH 6.6 and at 30°C cleaved phosphatidylinositol such that more than 85% of the product was inositol-1-phosphate. Other phospholipids were cleaved 5 to 10% or less under these conditions. The phospholipase had both a soluble and a membrane-associated form. The soluble activity accounted for approximately 85 to 90% of the activity and 15% was associated with membranes. The membrane-associated activity was most concentrated in the plasma membranes of hypocotyl segments of both soybean (Glycine max) and bushbean (Phaseolus vulgaris). The plasma membrane location was verified by analysis of highly purified plasma membranes prepared both by aqueous two-phase partitioning and by preparative free-flow electrophoresis and from the quantitation of the activity in all major cell fractions. Internal membranes also contained phospholipase C activity but at specific activity levels of about 0.1 those present in plasma membranes. Golgi apparatus-enriched fractions from which plasma membrane contaminants were removed by two-phase partition contained the activity at specific activity levels 0.2 those of plasma membrane. Both the soluble and the membrane-associated activity was stimulated by calcium but not by calmodulin, either alone or in the presence of calcium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsson P. A., Andersson B., Larsson C., Akerlund H. E. Phase partition--a method for purification and analysis of cell organelles and membrane vesicles. Methods Biochem Anal. 1982;28:115–150. doi: 10.1002/9780470110485.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss W. F., Massel M. O. Polyphosphoinositides are present in plant tissue culture cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91908-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drøbak B. K., Ferguson I. B. Release of Ca2+ from plant hypocotyl microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1241–1246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91747-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim S., Wagner K. G. Evidence of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositols in the growth cycle of suspension cultured plant cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1175–1181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Hepatic Golgi fractions resolved into membrane and content subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):822–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. The enzymology of stimulated inositol lipid turnover. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Stimulated inositol lipid metabolism: an introduction. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morré D. J., Gripshover B., Monroe A., Morré J. T. Phosphatidylinositol turnover in isolated soybean membranes stimulated by the synthetic growth hormone 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15364–15368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincon M., Boss W. F. myo-Inositol Trisphosphate Mobilizes Calcium from Fusogenic Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):395–398. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland J. C., Lembi C. A., Morré D. J. Phosphotungstic acid-chromic acid as a selective electron-dense stain for plasma membranes of plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):195–200. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandelius A. S., Penel C., Auderset G., Brightman A., Millard M., Morré D. J. Isolation of highly purified fractions of plasma membrane and tonoplast from the same homogenate of soybean hypocotyls by free-flow electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):177–185. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


