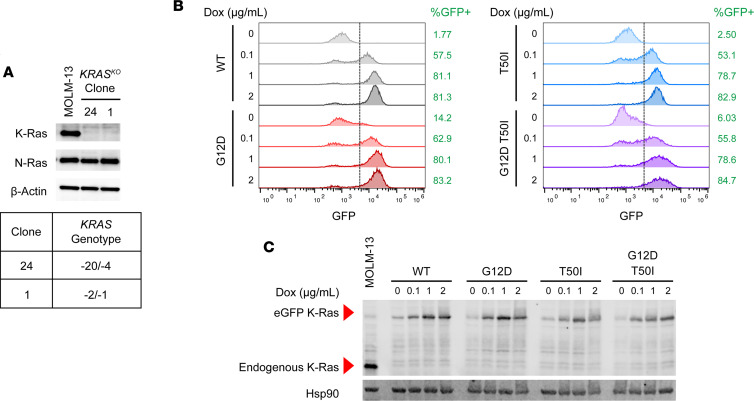
Figure 1. Regulatable K-Ras expression in FLT3-dependent MOLM-13 KRASKO cells.
(A) KRASKO clones 1 and 24 were generated from MOLM-13 cells by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing. Western blotting verified loss of K-Ras protein expression (top), and Sanger sequencing confirmed biallelic frameshift insertion–deletion mutations in both clones (bottom). (B) Flow cytometry analysis of KRASKO clone 24 cells expressing individual dox-inducible EGFP–K-Ras fusion proteins. Exposure to 2 μg/mL dox consistently induced EGFP–K-Ras expression in greater than 80% of events analyzed in clone 24 cells expressing EGFP–K-RasWT, EGFP–K-RasG12D, EGFP–K-RasT50I, or EGFP–K-RasG12D,T50I. (C) Western blotting of lysates prepared from the clone 24 cells shown in B demonstrates comparable levels of EGFP–K-Ras in KRASKO cells (~50 kDa due to addition of the EGFP cassette) and endogenous K-Ras (21 kDa) in parental MOLM-13 cells.