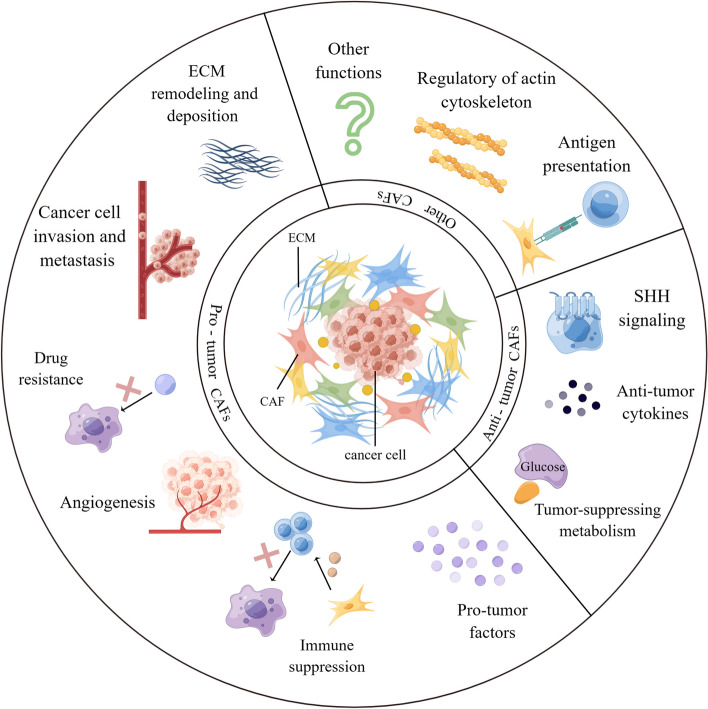
Fig. 3.
CAF interacts with a variety of tumor-promoting components through multiple signaling pathways. CAF can exert its pro-tumor function by promoting tumor neovascularization, promoting tumor cell proliferation and metastasis, regulating tumor microenvironment to an immunosuppressive state, and reconstructing ECM, etc. CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; CXCL, C–X–C motif chemokine; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; HMGB1, high mobility group protein 1; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IL, interleukin; NOTCH3, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3; LOXL2, lysyl oxidase like 2; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; POSTN, periostin; SDF-1, super dimensional fortress-1; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; TNFSF4, tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 4; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. By Figdraw