Figure 6. Human WNT2 and FZD5 are essential for liver cholesterol uptake and bile acid conjugation in vivo.
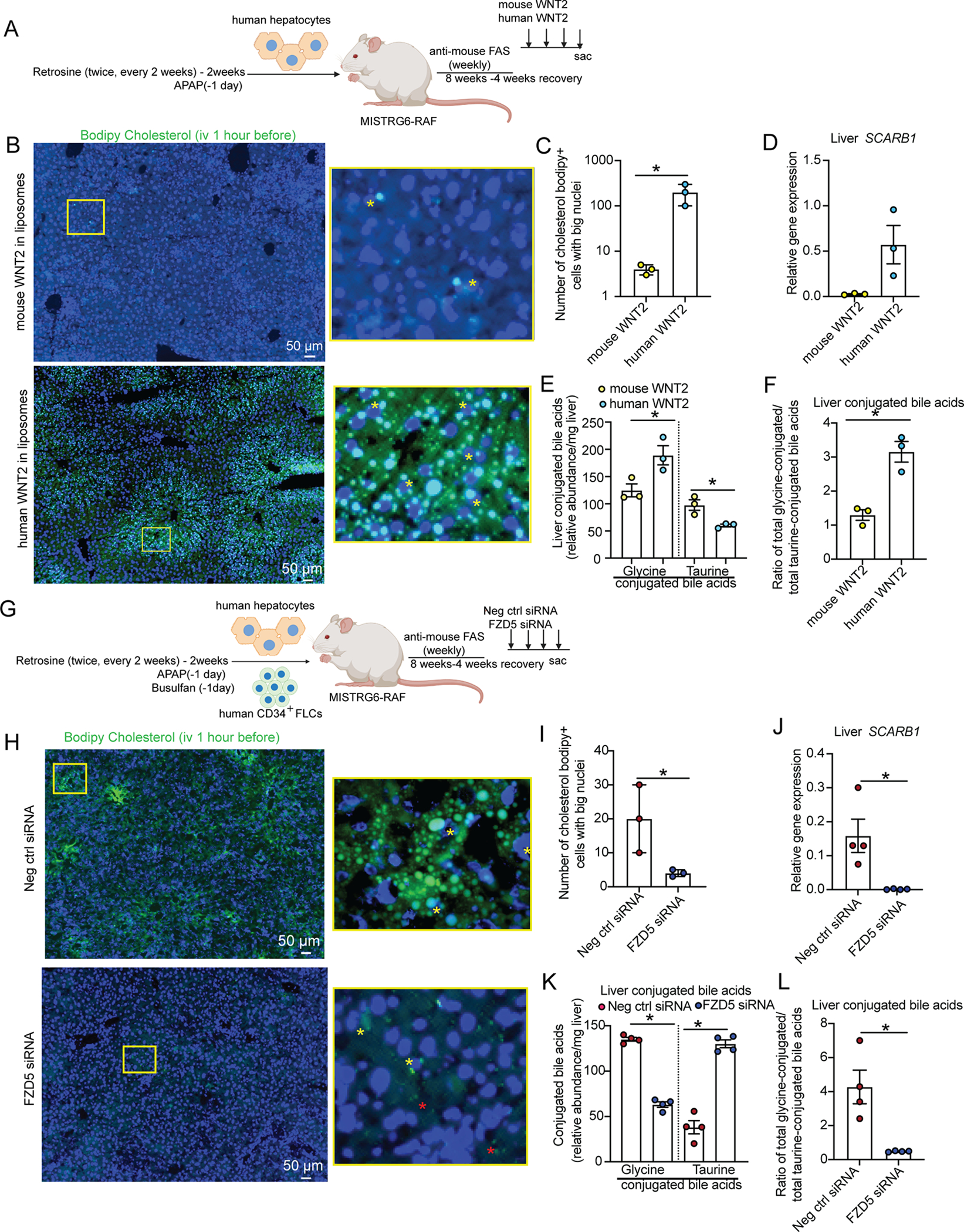
(A) MISTRG6-RAF mice bearing human hepatocytes were daily treated with human or mouse WNT2 in liposomes, i.v. for 3 days. 24 hours after the last injection, liver and plasma were collected.
(B, C, H-I) 1 hour before liver collection, mice were treated with bodipy-cholesterol i.v. Cells with big nuclei (indicative of hepatocytes) having green vesicles in the cytosol or close to the nucleus (indicated by yellow asterisk*) were counted. Small green vesicles (indicated by red asterisk) distant from big nuclei may indicate uptake from NPCs, therefore they were not counted. (Data are from 4 different fields per mouse at a 20x magnification).
(D, J) Relative gene expression of SCARB1 in the liver by RT-qPCR.
(E, F, K, L) Bile acids in the liver measured by HPLC-MS/MS.
(G) MISTRG6-RAF mice bearing human hepatocytes and human NPCs were daily treated with FZD5 or Neg ctrl siRNAs through tail injections for 3 days. 24 hours after the last injection, liver and plasma were collected.
Cartoon in 6A, 6G was made using BioRender. Each dot in the graphs is a biological replicate. Data represent mean ± SEM;*p <0.05.
