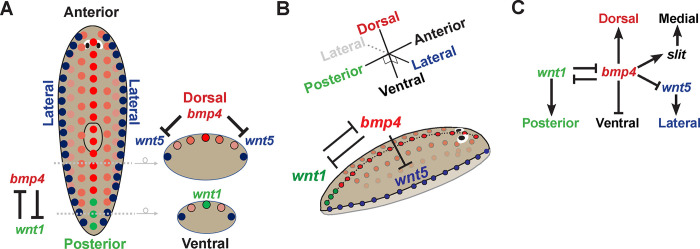
Fig 6. Model for homeostatic regulation of DV, AP, and ML axes by bmp4.
(A-B) 2D and 3D models illustrating mutual antagonism between bmp and wnt1 in the far posterior, bmp4 inhibition of wnt5 for control of lateral identity, and expression of key components across the AP and DV axes. Not shown, bmp4 activates slit expression on the midline, nog1;nog2 negatively regulate bmp4 to promote wnt1 posteriorly, and bmp4 regulates dorsal-versus-ventral tissue identity.(C) Regulatory model highlighting key interactions connecting axis information in homeostatic animals. bmp4 controls dorsal versus ventral identity, undergoes mutual inhibition with wnt1 for control of posterior identity, and activates slit and represses wnt5 in regulation mediolateral information.