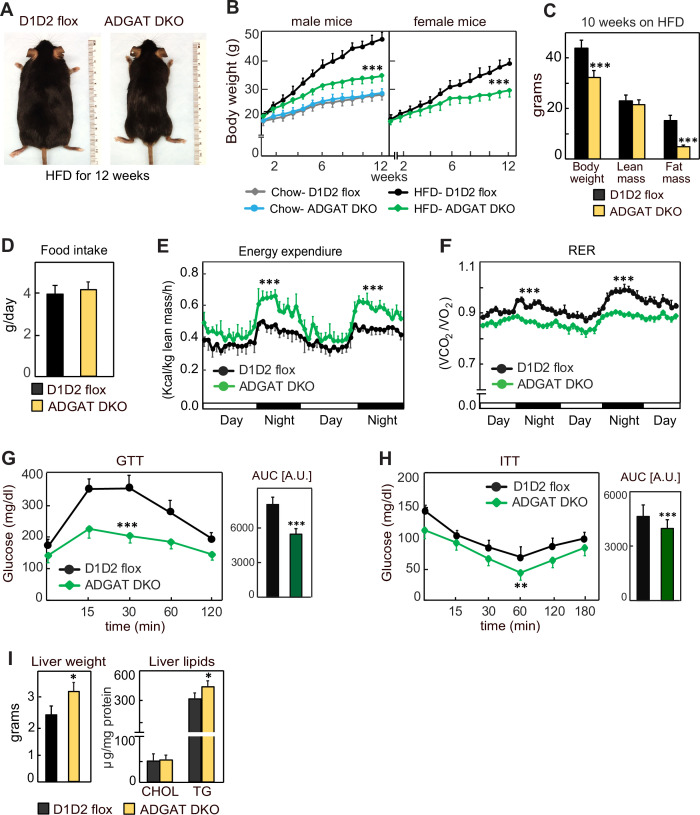
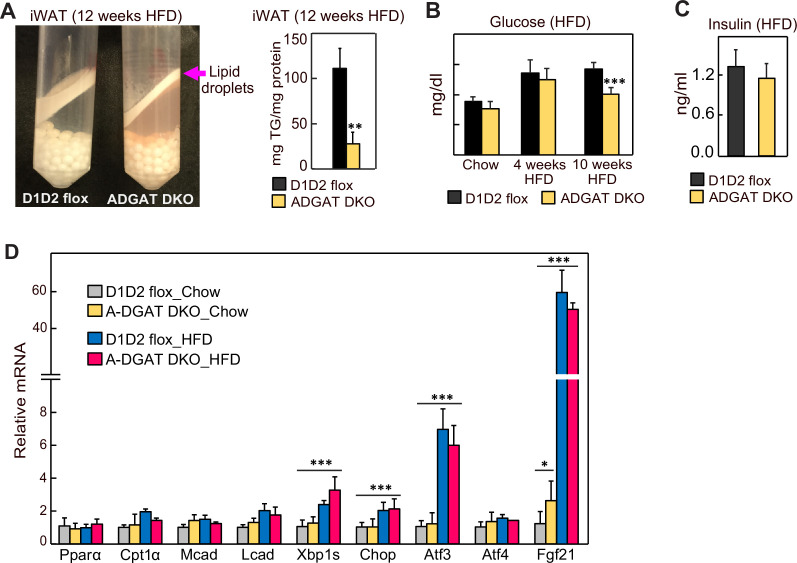
Figure 4. ADGAT DKO mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance.
(A) ADGAT DKO mice stay lean on a high-fat diet (HFD). Representative photographs of male mice fed on HFD for 12 weeks. (B) Both male and female ADGAT DKO mice gained ~40% less body weight than control mice. Body weights of mice fed on a chow-diet or HFD (n=15 for males, n=12 for females). (C) ADGAT DKO mice had decreased fat mass on HFD feeding. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) analysis of lean mass and fat mass of HFD fed male mice (n=10). (D) ADGAT DKO male mice had normal food intake during HFD feeding (n=5). (E and F) ADGAT DKO mice had increased energy expenditures. Energy expenditure and respiratory quotient on HFD-fed male mice measured by indirect calorimetry. Values were normalized to lean mass (n=4). (G and H) ADGAT DKO mice were protected from HFD-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Glucose- and insulin-tolerance tests were performed on HFD-fed (for 9 or 10 weeks, respectively) male mice (n=10). AUC, area under the curve. (I) Liver weights and triglyceride levels were moderately increased in HFD-fed ADGAT DKO male mice (n=6). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.