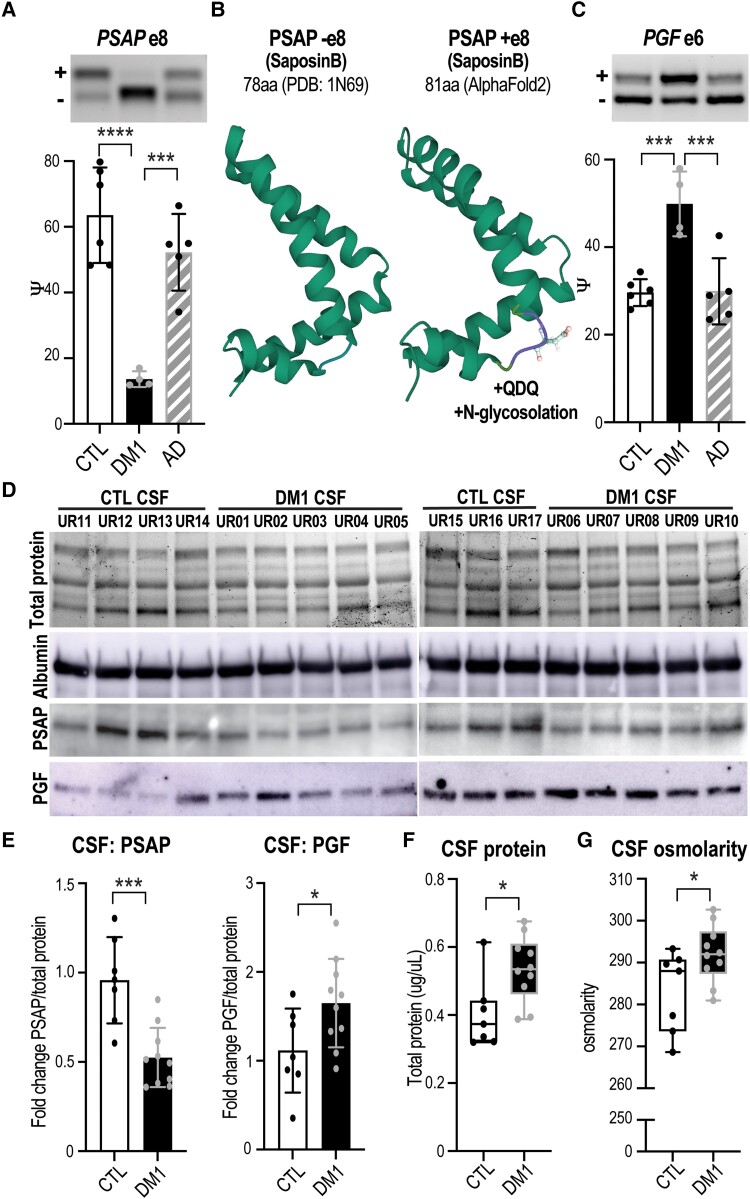
Figure 6.
Mis-splicing alters the ChP secretome and CSF composition. Neurologically unaffected (CTL) versus DM1 LVChP transcriptomic analysis of alternative splicing (AS) and differential expression (DE) was screened for ‘secreted’ GO annotation candidates. (A) PSAP was selected as a top secreted candidate and validated by RT-PCR gel (representative, top) and analysis (bar graph, bottom), which showed exclusion of exon 8 in DM1 ChP. (B) Predicted (AlphaFold2) protein structural changes due to PSAP exon 8 AS with the inclusion of a +QDQ (glutamine-aspartate-glutamine) in PSAP region SaposinB (PDB: 1N69). aa = amino acids. (C) Another top secreted candidate was PGF, which was validated by RT-PCR for increased exon 6 inclusion in DM1. (D) To test if ChP changes correlate with CSF composition, we obtained DM1 and non-DM1 (CTL) patient CSF for protein lysates and assayed top candidates, PSAP and PGF. Loading was normalized based on protein quantification, total protein signal and albumin western blot. (E) Western blot of PSAP and PGF proteins in DM1 patients’ CSF compared to CTLs was quantified as fold-change normalized over total protein signal. (F and G) To test if ChP changes also correlate with cumulative measures of CSF composition, CTL versus DM1 patients’ CSF was assayed for (F) total protein as well as (G) total osmolarity. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA or unpaired t-test.