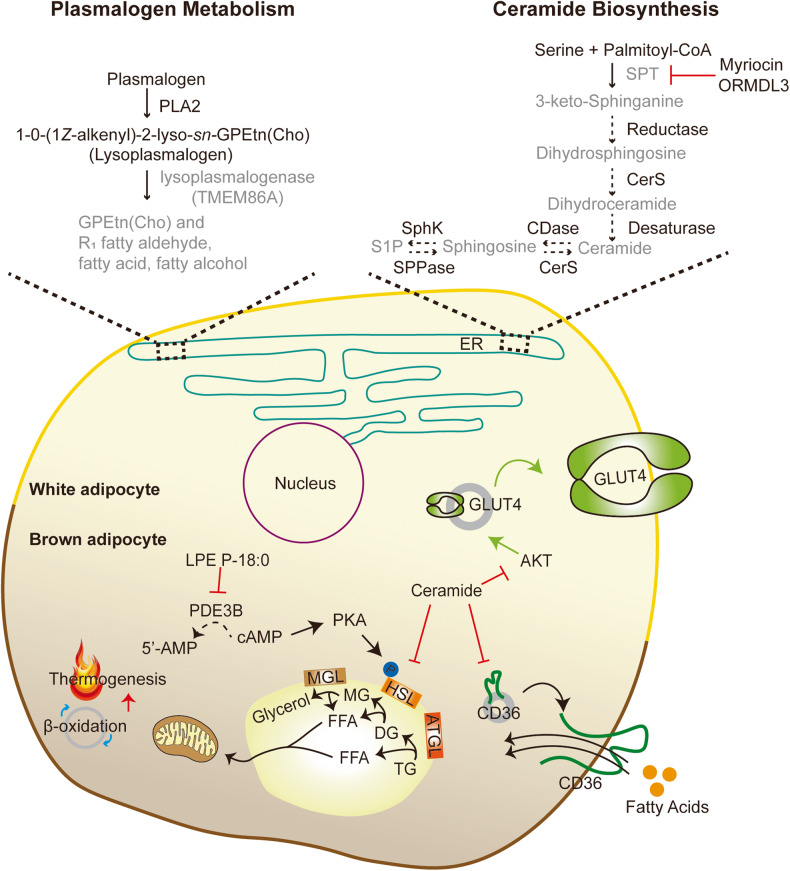
Fig. 2. Effects of genetic deletion of lipid biosynthetic and metabolic enzymes on adipocyte metabolism.
Enzymes and pathways involved in plasmalogen metabolism: TMEM86A has lysoplasmalogenase activity in adipocytes. Inhibiting the activity of TMEM86A leads to an increase in lysoplasmalogen and plasmalogen. LPE P-18:0, a lysoplasmalogen species, suppresses PDE3B activity, elevating intracellular cAMP levels. Increased levels of intracellular cAMP activate the PKA signaling pathway and induce lipolysis by phosphorylating HSL accompanied by enhanced thermogenesis. Enzymes and pathways involved in ceramide biosynthesis: Genetic abrogation of Sptlc2 and Ormdl3 regulates ceramide biosynthesis. Ceramides alleviate GLUT4 translocation via inhibition of AKT signaling, attenuate CD36 translocation, and suppress the activity of HSL, leading to impaired glucose tolerance, fatty acid uptake, and thermogenesis.