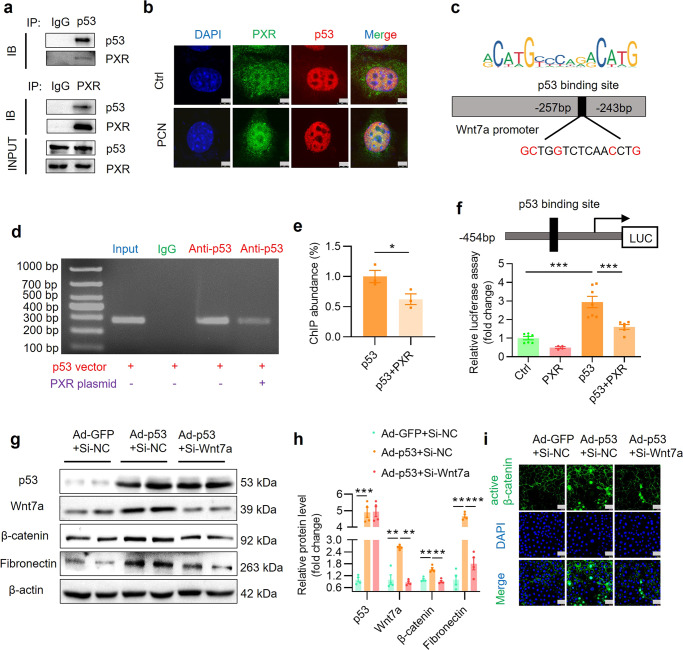
Fig. 10. PXR physically interacts with p53 protein and inhibits p53-induced Wnt7a gene transcription and β-catenin activation.
a Co-IP assay showing protein-protein interaction between PXR and p53 in HEK293T cells co-transfected with both mouse PXR and human p53 expression vector. b Immunofluorescence assay demonstrating that PCN treatment increased nuclear co-localization of p53 and PXR protein. Scale bar: 5 μm. c Identification of a putative p53 binding element using the JASPAR website. The predicted p53 binding site in mouse Wnt7a promoter is located between −257 bp and −243 bp. ChIP assay (d) and quantitative analysis (e) revealed that PXR markedly blocked the binding of p53 to mouse Wnt7a gene promoter. Mouse IgG served as a negative control (n = 3). f PXR overexpression significantly inhibited p53-induced Wnt7a promoter-driven luciferase reporter activity in HEK293T cells (n = 4–7). g Western blot analysis demonstrated that adenovirus-mediated p53 overexpression increased expression of Wnt7a, β-catenin and fibronectin. Wnt7a siRNA treatment eliminated p53-induced β-catenin activation and fibronectin expression in MTEC. h Quantitative analysis of the protein levels in g (n = 4). i Immunofluorescence assay showed that p53 overexpression increased the expression and activation of β-catenin, which was abolished by Wnt7a siRNA. Scale bar: 25 μm Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.