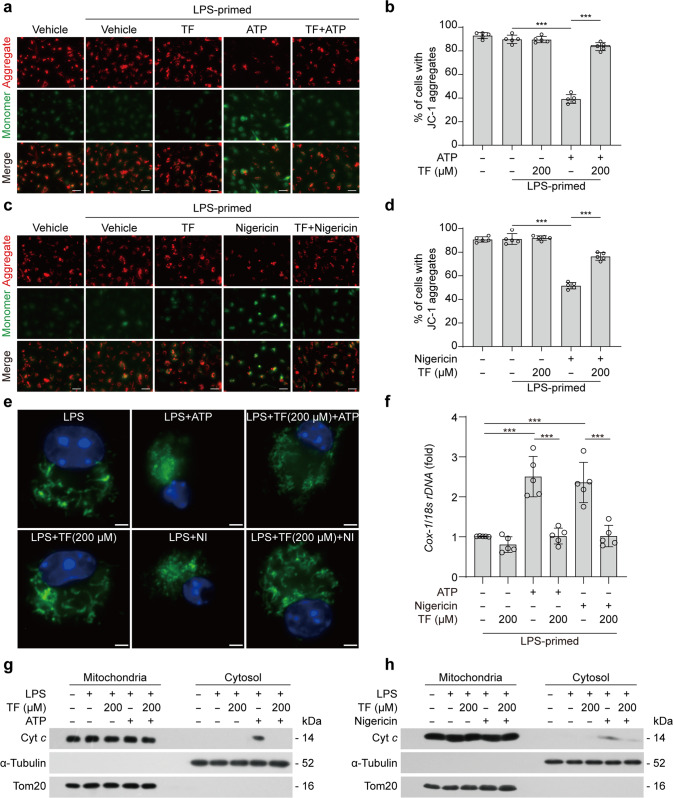
Fig. 4. Theaflavin alleviates mitochondrial damage induced by ATP or nigericin.
BMDMs were first primed with LPS (500 ng/mL) for 4 h, and then pretreated with indicated doses of theaflavin for 1 h, followed by incubation with ATP (4 mM) for 30 min or nigericin (5 μM) for 1 h. JC-1 was used to assay the mitochondrial membrane potential in the cells treated with ATP (a, b) or nigericin (c, d). One set of representative fluorescence microscopy images show JC-1 aggregates (red) and monomers (blue) (a, c). Scale bars, 20 μm. Quantitative analyses of JC-1 aggregates-containing cells treated with ATP (b) or nigericin (d), respectively. e Fluorescence microscopy was used to reveal mitochondria in BMDMs stained with Mito-Tracker Green (staining mitochondria; green) and Hoechst 33342 (staining nuclei; blue). Scale bars, 2 µm. f Cytosolic release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) was determined by qPCR with primers specific for mtDNA (cytochrome c oxidase 1, Cox-1) and nucleic DNA (nDNA) (18 s rDNA) in LPS-primed BMDMs treated ATP or nigericin. Western blotting of cytochrome c in mitochondria and cytosol enriched fractions from BMDMs treated with ATP (g) or nigericin (h). α-Tubulin and Tom20 were used as a loading control for cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions, respectively. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5). ***P < 0.001; NI, nigericin; Cyto c, cytochrome c; TF, theaflavin.