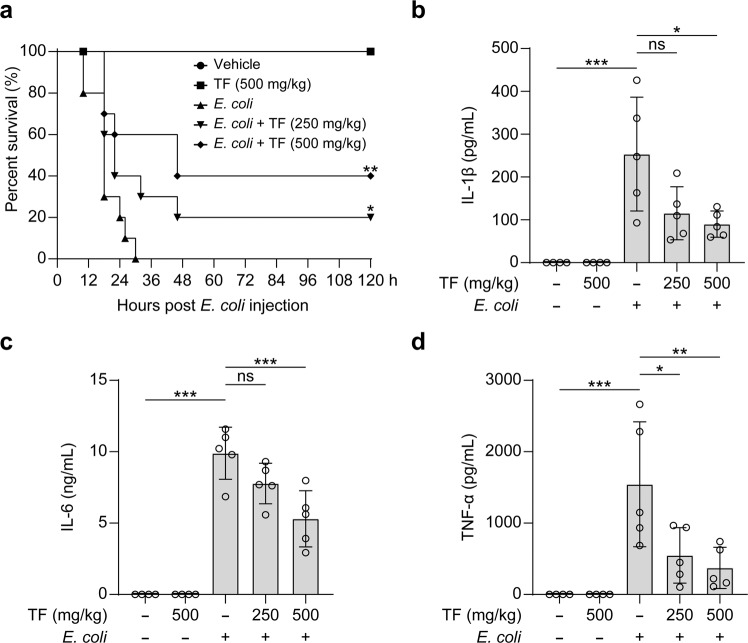
Fig. 9. Theaflavin alleviates sepsis in mice.
a C57BL/6 J mice were administered intragastrically (i.g.) with theaflavin (250 or 500 mg/kg body weight) or vehicle (2% Tween 80 in PBS) once a day for three consecutive days prior to intraperitoneal (i.p.) bacterial infection with viable Escherichia coli (2.0 × 109 CFU/mouse). Mice were administered (i.g.) with theaflavin or vehicle once again at 1 h after the bacterial injection. Mice survival was monitored every 6 h for 5 consecutive days. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were used to analyze the data (10 mice per group). The significance was evaluated by the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. b–d Mice were treated as in (a) except that mice were injected (i.p.) with viable E. coli (1.0 × 109 CFU/mouse). The serum levels of IL-1β (b), IL-6 (c), and TNF-α (d) at 8 h post bacterial infection were measured by CBA assay (4 or 5 mice per group). Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5). ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; TF theaflavin.