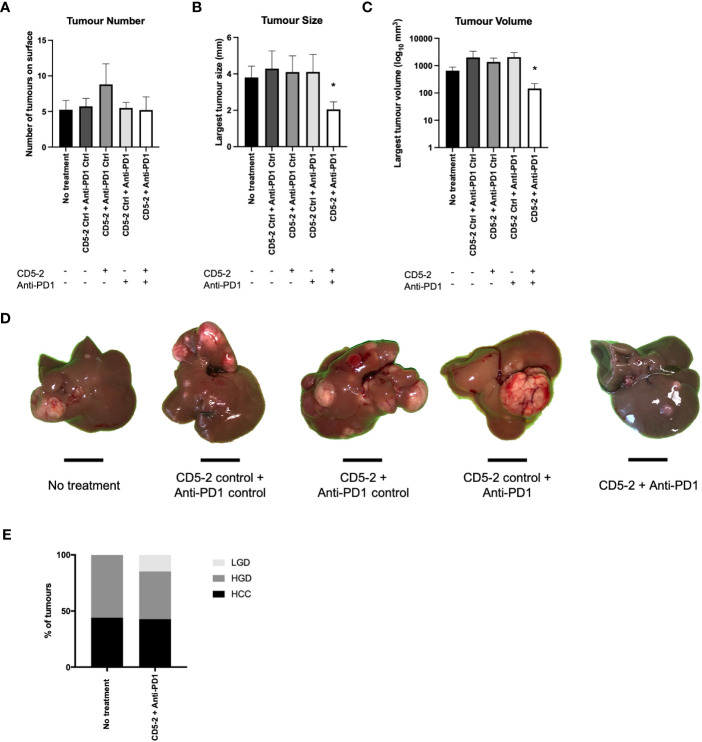
Figure 2.
Effects of combination CD5-2 and anti-PD1 on liver tumour formation. DEN was injected intraperitoneally once into wildtype C57BL/6 male pups at postnatal day 12-14. Control or CD5-2 Blockmir was administered intravenously every 2 weeks (30mg/kg) in combination with control Ig or anti-mouse PD1 mAb was administered intraperitoneally every 3 days (250µg) for a total of 8 weeks (weeks 30-38 of age). (A-D) Liver tissues were harvested at 38 weeks. Visible tumours on the surface of each liver were counted and their size measured. Graphs of (A) liver tumour number, (B) maximum tumour size, and (C) liver tumour volume. (D) Macroscopic images of visible liver tumour in each treatment group. (E) Proportion of liver tumours classified by two expert liver pathologists as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), high-grade dysplastic (HGD) nodules and low-grade dysplastic (LGD) nodules in DEN-treated mice from no treatment vs. CD5-2 plus anti-PD1 groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n=20 each group. Scale bar = 0.5cm * = P<0.05.