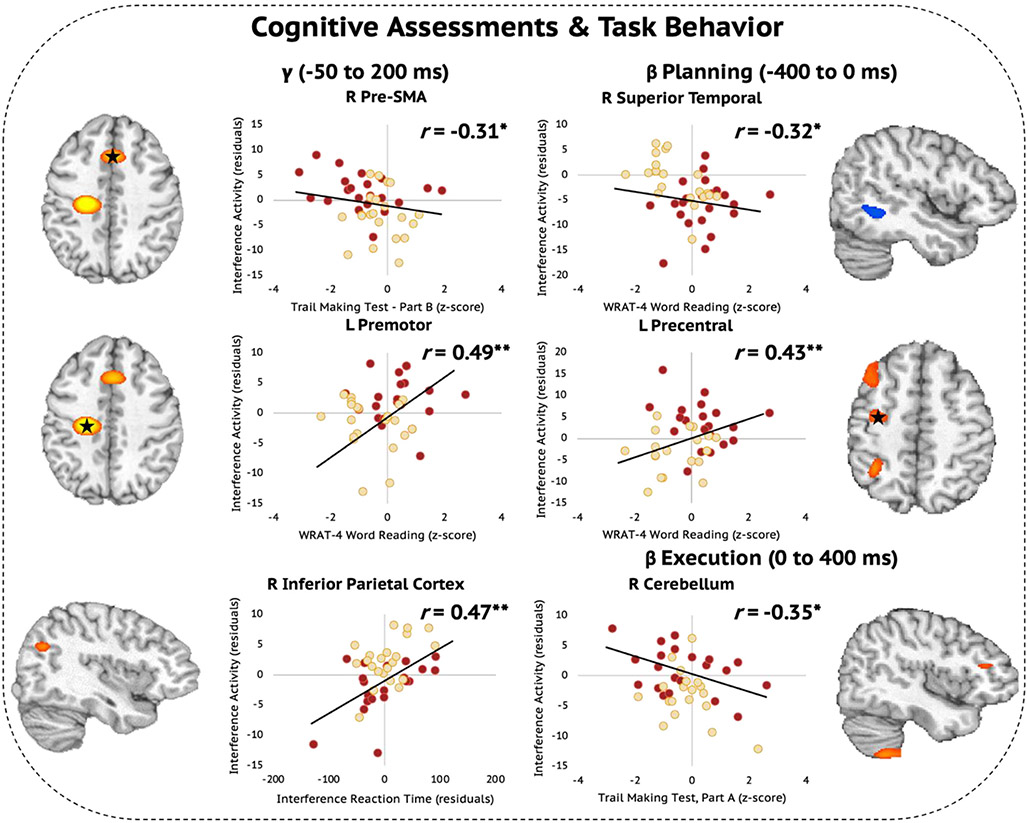
Fig. 7.
Oscillatory Beta and Gamma Interference Effects Scale with Cognitive Assessments Among Those with HAND and ADS. (Left) Weaker oscillatory gamma interference effects in the right pre-SMA were associated with better performance on the Trail Making Test, Part B. Higher premorbid function measured using the WRAT-4 Word Reading test was associated with stronger gamma interference effects in the left premotor cortex. Stronger gamma interference effects in the right inferior parietal cortex scaled with greater behavioral interference in terms of reaction time (in ms). (Right) Better WRAT-4 Word Reading scores were associated with stronger (i.e., more negative) beta interference effects in the right superior temporal area during the motor planning period, but the inverse of this relationship was observed in the left precentral cortex in which weaker (i.e., more positive) beta interference effects during the motor planning period were associated with higher premorbid function. Finally, better performance on the Trail Making Test, Part A scaled with stronger beta interference effects in the right cerebellum during the motor execution period. *p < .05, **p < .01.