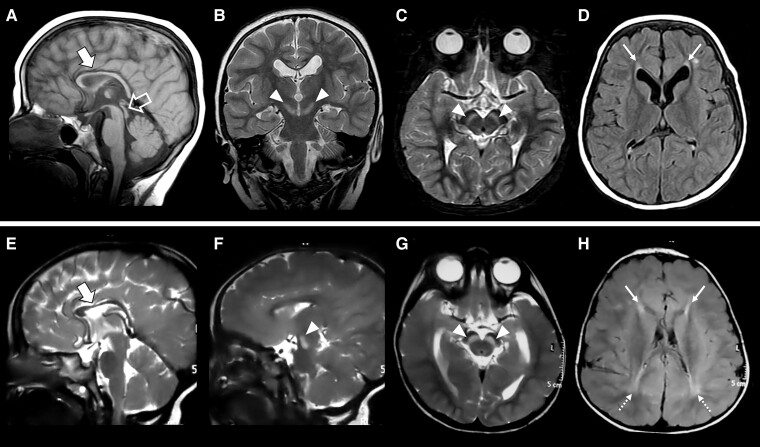
Figure 2.
Neuroimaging features of LNPK-related disorder. Brain MRI studies performed in Patient II:1 from Family 6 at 4 years of age (A–D) and in Patient II:2 from Family 7 at 2.5 years of age (E–H). Sagittal T1- (A) or T2-weighted (E) images demonstrate corpus callosum hypoplasia with prevalent involvement of the anterior portions (thick arrows). Coronal (B), axial (C, G) and sagittal (F) T2-weighted images reveal symmetric marked T2 hyperintensity of the substantia nigra (arrowheads). Note the ‘ears-of-the-lynx’ sign (thin arrows) on axial FLAIR images (D, H) consisting of hyperintense signal of the forceps minor bilaterally, which resembles the shape of the ears of a lynx with their characteristic apical hair tuft. Additional posterior periventricular white matter signal alterations are noted in Patient II:2 from Family 7 (dotted arrows). A short midbrain is also visible in Patient II:1 from Family 6 (empty arrow).