Figure 2.
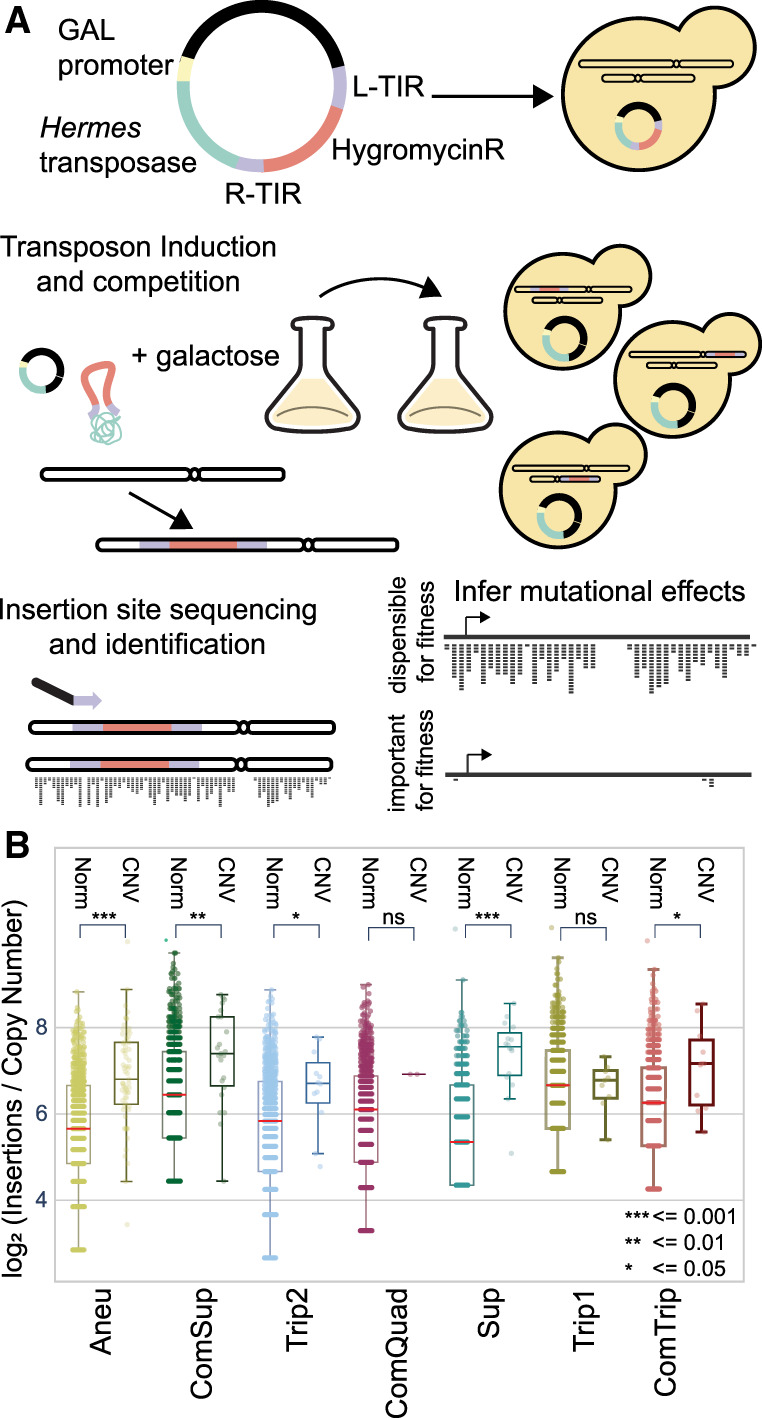
Profiling mutation tolerance in CNV strains using insertional mutagenesis. (A) Plasmids containing the Hermes transposase regulated by the GALS promoter (a truncated GAL1 promoter) and a hygromycin-resistance gene flanked by the Hermes terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) were transformed into each yeast strain. Upon addition of galactose, the transposase is expressed, and the hygromycin-resistance gene flanked by the TIRs is excised from the plasmid and inserted in the yeast genome. DNA is extracted, digested with restriction enzymes, and circularized. Insertion sites are identified by inverse PCR and amplicon sequencing. Mutational tolerance for a gene is inferred using the number of unique insertion sites over the protein-coding region. (B) Unique insertion sites per gene copy number (CN) for essential genes. Genes are defined as either CNV associated (CNV) or not (Norm). A Mann–Whitney U statistic was used to compare distributions between the CNV and Norm essential genes, P-values are indicated by the following: (ns) P > 0.05, (*) P ≤ 0.05, (**) P ≤ 0.01, (***) P ≤ 0.001.
