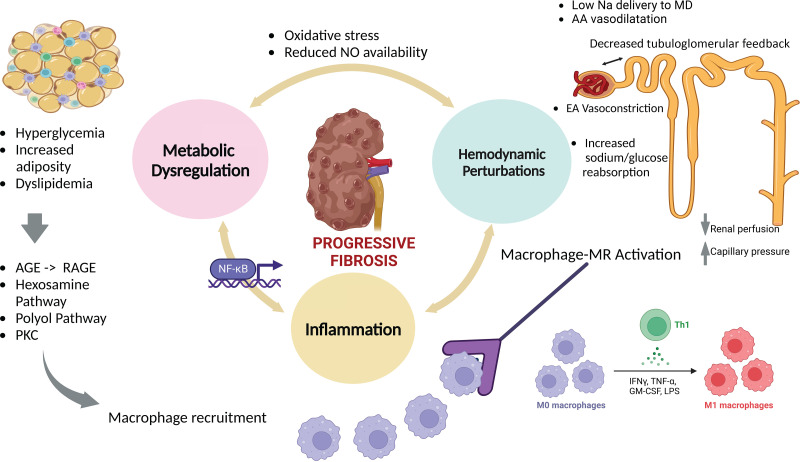
Figure 2.
Metabolic, hemodynamic, and inflammatory pathways implicated in the underlying pathophysiology of DKD, underscoring the need for multitargeted therapies to halt disease progression. MR is a pervasive ligand-activated transcription factor that exerts injury beyond the kidney to endothelial cells, adipocytes, smooth muscle cells, and immune cells (55,136). Once released in local tissue, inflammatory cytokines exert pleiotropic effects, setting in motion inflammatory and profibrotic processes that affect adjacent compartments and contribute to increased adverse cross talk between glomeruli, which contributes further to increased scarring (137). AA, afferent arteriole; AGE, advanced glycation end products; EA, efferent arteriole; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFNγ, γ-interferon; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MD, macula densa; NO, nitric oxide; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ light-chain enhancer of activated β-cell; RAGE, receptor-bound advanced glycation end products.