FIGURE 5.
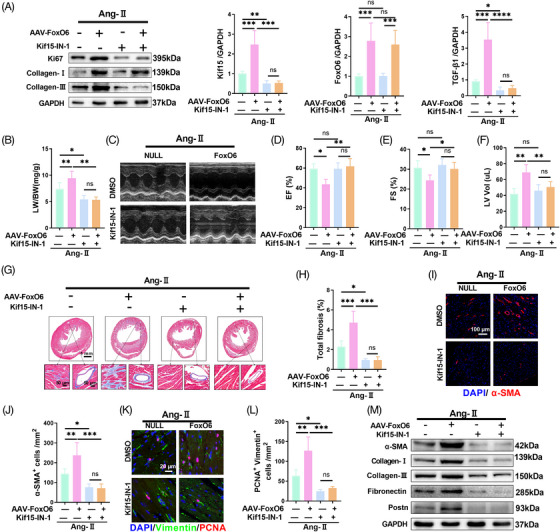
Inhibition of Kif15 eliminated pro‐fibrotic and adverse cardiac function effects caused by Forkhead box protein O6 (FoxO6) overexpression. (A) Cardiac protein expression levels of FoxO6, Kif15, and transforming growth factor‐β1 (TGF‐β1) in murine myocardium (n = 6). (B) Lung‐to‐body weight (LW/BW) ratio of mice (n = 6). (C) Echocardiography of mice. (D–F) Ejection fraction (EF)%, fraction shortening (FS)%, and left ventricle volume (LV vol), respectively, determined by echocardiography (n = 8). (G) Typical images of murine heart sections stained with Masson's trichrome stain, perivascular area and interstitial area were amplified. (H) Degree of LV fibrosis evidenced by collagen volume (n = 7). (I) Immunostaining of murine myocardium sections to exhibit the expression of α‐SMA (red). (J) Number of α‐SMA‐positive cells (n = 6). (K) Immunostaining of murine myocardium sections to exhibit the expression of vimentin (green) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) (red). (L) Number of vimentin‐ and PCNA‐positive cells (n = 6). (M) Cardiac protein expression levels of α‐SMA, collagen I, collagen III, fibronectin, and Postn in murine myocardium (n = 6). Data were analyzed by one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. Statistics are carried out as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
